Hydrogen sulfide protects against chemical hypoxia-induced injury by inhibiting ROS-activated ERK1/2 and p38MAPK signaling pathways in PC12 cells
- PMID: 21998720
- PMCID: PMC3187826
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025921
Hydrogen sulfide protects against chemical hypoxia-induced injury by inhibiting ROS-activated ERK1/2 and p38MAPK signaling pathways in PC12 cells
Abstract
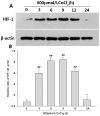
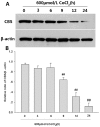
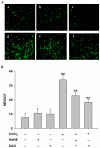
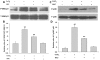
Hydrogen sulfide (H(2)S) has been proposed as a novel neuromodulator and neuroprotective agent. Cobalt chloride (CoCl(2)) is a well-known hypoxia mimetic agent. We have demonstrated that H(2)S protects against CoCl(2)-induced injuries in PC12 cells. However, whether the members of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK), in particular, extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2(ERK1/2) and p38MAPK are involved in the neuroprotection of H(2)S against chemical hypoxia-induced injuries of PC12 cells is not understood. We observed that CoCl(2) induced expression of transcriptional factor hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α), decreased cystathionine-β synthase (CBS, a synthase of H(2)S) expression, and increased generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to injuries of the cells, evidenced by decrease in cell viability, dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) , caspase-3 activation and apoptosis, which were attenuated by pretreatment with NaHS (a donor of H(2)S) or N-acetyl-L cystein (NAC), a ROS scavenger. CoCl(2) rapidly activated ERK1/2, p38MAPK and C-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Inhibition of ERK1/2 or p38MAPK or JNK with kinase inhibitors (U0126 or SB203580 or SP600125, respectively) or genetic silencing of ERK1/2 or p38MAPK by RNAi (Si-ERK1/2 or Si-p38MAPK) significantly prevented CoCl(2)-induced injuries. Pretreatment with NaHS or NAC inhibited not only CoCl(2)-induced ROS production, but also phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38MAPK. Thus, we demonstrated that a concurrent activation of ERK1/2, p38MAPK and JNK participates in CoCl(2)-induced injuries and that H(2)S protects PC12 cells against chemical hypoxia-induced injuries by inhibition of ROS-activated ERK1/2 and p38MAPK pathways. Our results suggest that inhibitors of ERK1/2, p38MAPK and JNK or antioxidants may be useful for preventing and treating hypoxia-induced neuronal injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







References
-
- Kimura H. Hydrogen sulfide as a neuromodulator. Mol Neurobiol. 2002;26:13–9. - PubMed
-
- Ishigami M, Hiraki K, Umemura K, Oqasawara Y, Ishii K, et al. A source of Hydrogen sulfide and a mechanism of its release in the brain. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009;11:205–14. - PubMed
-
- Furne J, Saeed A, Levitt MD. Whole tissue hydrogen sulfide concentrations are orders of magnitude lower than presently accepted values. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008;295:R1479–85. - PubMed
-
- Kimura H. Hydrogen sulfide induces cyclic AMP and modulates the NMDA receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;267:129–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

