A clonal group of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae with two IgA proteases is adapted to infection in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- PMID: 21998721
- PMCID: PMC3187821
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025923
A clonal group of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae with two IgA proteases is adapted to infection in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Abstract
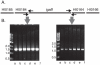
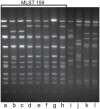
Strains of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae show enormous genetic heterogeneity and display differential virulence potential in different clinical settings. The igaB gene, which encodes a newly identified IgA protease, is more likely to be present in the genome of COPD strains of H. influenzae than in otitis media strains. Analysis of igaB and surrounding sequences in the present study showed that H. influenzae likely acquired igaB from Neisseria meningitidis and that the acquisition was accompanied by a ~20 kb genomic inversion that is present only in strains that have igaB. As part of a long running prospective study of COPD, molecular typing of H. influenzae strains identified a clonally related group of strains, a surprising observation given the genetic heterogeneity that characterizes strains of nontypeable H. influenzae. Analysis of strains by 5 independent methods (polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, multilocus sequence typing, igaB gene sequences, P2 gene sequences, pulsed field gel electrophoresis) established the clonal relationship among the strains. Analysis of 134 independent strains collected prospectively from a cohort of adults with COPD demonstrated that ~10% belonged to the clonal group. We conclude that a clonally related group of strains of nontypeable H. influenzae that has two IgA1 protease genes (iga and igaB) is adapted for colonization and infection in COPD. This observation has important implications in understanding population dynamics of H. influenzae in human infection and in understanding virulence mechanisms specifically in the setting of COPD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
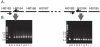

References
-
- Faden H, Duffy L, Williams A, Pediatrics TW, Krystofik DA, et al. Epidemiology of nasopharyngeal colonization with nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae in the first 2 years of life. J Infect Dis. 1995;172:132–135. - PubMed
-
- Murphy TF, Faden H, Bakaletz LO, Kyd JM, Forsgren A, et al. Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae as a pathogen in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009;28:43–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

