Gene expression of human lung cancer cell line CL1-5 in response to a direct current electric field
- PMID: 21998723
- PMCID: PMC3187831
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025928
Gene expression of human lung cancer cell line CL1-5 in response to a direct current electric field
Abstract
Background: Electrotaxis is the movement of adherent living cells in response to a direct current (dc) electric field (EF) of physiological strength. Highly metastatic human lung cancer cells, CL1-5, exhibit directional migration and orientation under dcEFs. To understand the transcriptional response of CL1-5 cells to a dcEF, microarray analysis was performed in this study.
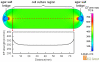
Methodology/principal findings: A large electric-field chip (LEFC) was designed, fabricated, and used in this study. CL1-5 cells were treated with the EF strength of 0 mV/mm (the control group) and 300 mV/mm (the EF-treated group) for two hours. Signaling pathways involving the genes that expressed differently between the two groups were revealed. It was shown that the EF-regulated genes highly correlated to adherens junction, telomerase RNA component gene regulation, and tight junction. Some up-regulated genes such as ACVR1B and CTTN, and some down-regulated genes such as PTEN, are known to be positively and negatively correlated to cell migration, respectively. The protein-protein interactions of adherens junction-associated EF-regulated genes suggested that platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptors and ephrin receptors may participate in sensing extracellular electrical stimuli. We further observed a high percentage of significantly regulated genes which encode cell membrane proteins, suggesting that dcEF may directly influence the activity of cell membrane proteins in signal transduction.
Conclusions/significance: In this study, some of the EF-regulated genes have been reported to be essential whereas others are novel for electrotaxis. Our result confirms that the regulation of gene expression is involved in the mechanism of electrotactic response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- McCaig CD, Rajnicek AM, Song B, Zhao M. Controlling cell behavior electrically: Current views and future potential. Physiological Reviews. 2005;85:943–978. - PubMed
-
- Szatkowski M, Mycielska M, Knowles R, Kho AL, Djamgoz MBA. Electrophysiological recordings from the rat prostate gland in vitro: identified single-cell and transepithelial (lumen) potentials. Bju International. 2000;86:1068–1075. - PubMed
-
- Cuzick J, Holland R, Barth V, Davies R, Faupel M, et al. Electropotential measurements as a new diagnostic modality for breast cancer. Lancet. 1998;352:359–363. - PubMed
-
- Nuccitelli R. Measuring endogenous electric fields. The Physiology of Bioelectricity in Development, Tissue Regeneration and Cancer. 2011;1:1–16.
-
- Djamgoz MBA, Mycielska M, Madeja Z, Fraser SP, Korohoda W. Directional movement of rat prostate cancer cells in direct-current electric field: involvement of voltage-gated Na+ channel activity. Journal of Cell Science. 2001;114:2697–2705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

