Hyperforin inhibits Akt1 kinase activity and promotes caspase-mediated apoptosis involving Bad and Noxa activation in human myeloid tumor cells
- PMID: 21998731
- PMCID: PMC3188562
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025963
Hyperforin inhibits Akt1 kinase activity and promotes caspase-mediated apoptosis involving Bad and Noxa activation in human myeloid tumor cells
Abstract
Background: The natural phloroglucinol hyperforin HF displays anti-inflammatory and anti-tumoral properties of potential pharmacological interest. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells abnormally proliferate and escape apoptosis. Herein, the effects and mechanisms of purified HF on AML cell dysfunction were investigated in AML cell lines defining distinct AML subfamilies and primary AML cells cultured ex vivo.
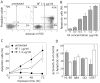
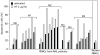
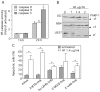
Methodology and results: HF inhibited in a time- and concentration-dependent manner the growth of AML cell lines (U937, OCI-AML3, NB4, HL-60) by inducing apoptosis as evidenced by accumulation of sub-G1 population, phosphatidylserine externalization and DNA fragmentation. HF also induced apoptosis in primary AML blasts, whereas normal blood cells were not affected. The apoptotic process in U937 cells was accompanied by downregulation of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2, upregulation of pro-apoptotic Noxa, mitochondrial membrane depolarization, activation of procaspases and cleavage of the caspase substrate PARP-1. The general caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-fmk and the caspase-9- and -3-specific inhibitors, but not caspase-8 inhibitor, significantly attenuated apoptosis. HF-mediated apoptosis was associated with dephosphorylation of active Akt1 (at Ser(473)) and Akt1 substrate Bad (at Ser(136)) which activates Bad pro-apoptotic function. HF supppressed the kinase activity of Akt1, and combined treatment with the allosteric Akt1 inhibitor Akt-I-VIII significantly enhanced apoptosis of U937 cells.
Significance: Our data provide new evidence that HF's pro-apoptotic effect in AML cells involved inhibition of Akt1 signaling, mitochondria and Bcl-2 members dysfunctions, and activation of procaspases -9/-3. Combined interruption of mitochondrial and Akt1 pathways by HF may have implications for AML treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Calixto JB, Campos MM, Otuki MF, Santos AR. Anti-inflammatory compounds of plant origin. Part II. modulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines and adhesion molecules. Planta Med. 2004;70:93–103. - PubMed
-
- Calixto JB, Otuki MF, Santos AR. Anti-inflammatory compounds of plant origin. Part I. Action on arachidonic acid pathway, nitric oxide and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB). Planta Med. 2003;69:973–983. - PubMed
-
- Bailly C. Ready for a comeback of natural products in oncology. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009;77:1447–1457. - PubMed
-
- Medina MA, Martinez-Poveda B, Amores-Sanchez MI, Quesada AR. Hyperforin: more than an antidepressant bioactive compound? Life Sci. 2006;79:105–111. - PubMed
-
- Quiney C, Billard C, Salanoubat C, Fourneron JD, Kolb JP. Hyperforin, a new lead compound against the progression of cancer and leukemia? Leukemia. 2006;20:1519–1525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

