Blood Mercury Level and Its Determinants among Dental Practitioners in Hamadan, Iran
- PMID: 21998776
- PMCID: PMC3184749
Blood Mercury Level and Its Determinants among Dental Practitioners in Hamadan, Iran
Abstract
Objective: Exposure to mercury can occur in occupational and environmental settings. During clinical work with dental amalgam, the dental personnel are exposed to both metallic mercury and mercury vapor. The aim of the present study was to investigate blood mercury level (BML) and its determinants among dentists practicing in Hamadan city, Iran.
Materials and methods: This cross sectional study was done on all dental practitioners of Hamadan (n=43). Dentists were asked to complete a questionnaire, and then 5 ml blood samples were obtained from them. After preparation, mercury concentration of each sample was measured by cold vapor atomic absorption device. Pearson correlation test and regression models served for statistical analysis.
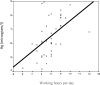
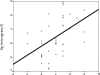
Results: The mean blood concentration of mercury was 6.3 μg/l (SD=1.31 range 4.15-8.93). BML was positively associated with age, years in practice, working hours per day, number of amalgam restorations per day, number of amalgam removal per week, sea food consumption, working years in present office, using amalgam powder, using diamond bur for amalgam removal, dry sterilization of amalgam contaminated instruments, and deficient air ventilation.
Conclusion: BML of dentists in Hamadan was higher than standards. Working hours and number of amalgam restorations per day were significantly correlated with blood mercury.
Keywords: Dental Amalgam; Iran; Mercury.
Figures

References
-
- Bayane SC, Thompson JY. Biomaterials. Art and science of operative dentistry. In: Roberson TM, Heyman HO, Swift EJ, editors. 4rd ed. North Carolina: Mosby Co; 2006. pp. 135–242.
-
- Powers JM, Sakaguchi RL. Amalgams. In: Powers JM, Sakaguchi RL, editors. Craig’s Restorative dental materials. 12th ed. St louis, Missouri: Mosby Co; 2006. pp. 235–67.
-
- Karahalil B, Rahravi H, Ertas N. Examination of urinary mercury levels in dentists in Turkey. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2005 Aug;24(8):383–8. - PubMed
-
- Möller-Madsen B, Hansen JC, Kragstrup J. Mercury concentrations in blood from Danish dentists. Scand J Dent Res. 1988 Feb;96(1):56–9. - PubMed
-
- Langan DC, Fan PL, Hoos AA. The use of mercury in dentistry: a critical review of the recent literature. J Am Dent Assoc. 1987 Dec;115(6):867–80. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
