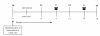Investigating a TELEmedicine solution to improve MEDication adherence in chronic Heart Failure (TELEMED-HF): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 21999637
- PMCID: PMC3213026
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-12-227
Investigating a TELEmedicine solution to improve MEDication adherence in chronic Heart Failure (TELEMED-HF): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Frequent rehospitalisations and poorer survival chances in heart failure (HF) patients may partly be explained by poor medication adherence. There are multiple medication-related reasons for suboptimal adherence, but psychological reasons may also be important. A novel TELEmonitoring device may improve MEDication adherence in HF patients (TELEMED-HF). TELEMED-HF is a randomized, controlled clinical intervention trial designed to examine (1) the efficacy and cost-efficiency of an electronic medication adherence support system in improving and monitoring HF patients' medication adherence; (2) the effect of medication adherence on hospitalizations and health care consumption; as well as on (3) clinical characteristics, and Quality of Life (QoL); and (4) clinical, sociodemographic, and psychological determinants of medication adherence.
Methods/design: Consecutive patients with chronic, systolic HF presenting to the outpatient clinic of the TweeSteden Hospital, The Netherlands, will be approached for study participation and randomly assigned (1:1) following blocked randomization procedures to the intervention (n = 200) or usual care arm (n = 200). Patients in the intervention arm use the medication support device for six months in addition to usual care. Post-intervention, patients return to usual care only and all patients participate in four follow-up occasions over 12 months. Primary endpoints comprise objective and subjective medication adherence, healthcare consumption, number of hospitalizations, and cost-effectiveness. Secondary endpoints include disease severity, physical functioning, and QoL.
Discussion: The TELEMED-HF study will provide us a comprehensive understanding of medication adherence in HF patients, and will show whether telemonitoring is effective and cost-efficient in improving adherence and preventing hospitalization in HF patients.
Trial registration number: NCT01347528.
Figures
References
-
- Wieren SvR, Rutten FH, (Julius centrum) Volksgezondheid Toekomst Verkenning, Nationaal Kompas Volksgezondheid. Bilthoven: RIVM; 2008. Welke zorg gebruiken patiënten en wat zijn de kosten?
-
- Dickstein K, Cohen-Solal A, Filippatos G, McMurray JJ, Ponikowski P, Poole-Wilson PA, Stromberg A, van Veldhuisen DJ, Atar D, Hoes AW. et al.ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2008 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association of the ESC (HFA) and endorsed by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM) Eur Heart J. 2008;29:2388–2442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous