Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms
- PMID: 22000009
- PMCID: PMC3261217
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.024
Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms
Abstract
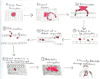
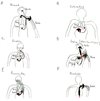
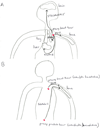
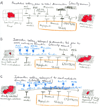
Metastases represent the end products of a multistep cell-biological process termed the invasion-metastasis cascade, which involves dissemination of cancer cells to anatomically distant organ sites and their subsequent adaptation to foreign tissue microenvironments. Each of these events is driven by the acquisition of genetic and/or epigenetic alterations within tumor cells and the co-option of nonneoplastic stromal cells, which together endow incipient metastatic cells with traits needed to generate macroscopic metastases. Recent advances provide provocative insights into these cell-biological and molecular changes, which have implications regarding the steps of the invasion-metastasis cascade that appear amenable to therapeutic targeting.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Al-Mehdi AB, Tozawa K, Fisher AB, Shientag L, Lee A, Muschel RJ. Intravascular origin of metastasis from the proliferation of endothelium-attached tumor cells: a new model for metastasis. Nat Med. 2000;6:100–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

