A primary role for release factor 3 in quality control during translation elongation in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 22000017
- PMCID: PMC3415990
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.045
A primary role for release factor 3 in quality control during translation elongation in Escherichia coli
Abstract
Release factor 3 (RF3) is a GTPase found in a broad range of bacteria where it is thought to play a critical "recycling" role in translation by facilitating the removal of class 1 release factors (RF1 and RF2) from the ribosome following peptide release. More recently, RF3 was shown in vitro to stimulate a retrospective editing reaction on the bacterial ribosome wherein peptides carrying mistakes are prematurely terminated during protein synthesis. Here, we examine the role of RF3 in the bacterial cell and show that the deletion of this gene sensitizes cells to other perturbations that reduce the overall fidelity of protein synthesis. We further document substantial effects on mRNA stability and protein expression using reporter systems, native mRNAs and proteins. We conclude that RF3 plays a primary role in vivo in specifying the fidelity of protein synthesis thus impacting overall protein quantity and quality.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



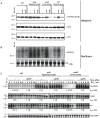
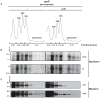


Similar articles
-
Interactions of release factor RF3 with the translation machinery.Mol Genet Genomics. 2015 Aug;290(4):1335-44. doi: 10.1007/s00438-015-0994-x. Epub 2015 Jan 31. Mol Genet Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25636454
-
Visualization of translation termination intermediates trapped by the Apidaecin 137 peptide during RF3-mediated recycling of RF1.Nat Commun. 2018 Aug 3;9(1):3053. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05465-1. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30076302 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of ribosomes and release factors during translation termination in E. coli.Elife. 2018 Jun 11;7:e34252. doi: 10.7554/eLife.34252. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29889659 Free PMC article.
-
Termination of translation: interplay of mRNA, rRNAs and release factors?EMBO J. 2003 Jan 15;22(2):175-82. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg017. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12514123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The function, structure and regulation of E. coli peptide chain release factors.Biochimie. 1987 Oct;69(10):1031-41. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90003-4. Biochimie. 1987. PMID: 3126822 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct roles for release factor 1 and release factor 2 in translational quality control.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jun 20;289(25):17589-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.564989. Epub 2014 May 5. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24798339 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental perturbations lift the degeneracy of the genetic code to regulate protein levels in bacteria.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Feb 5;110(6):2419-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1211077110. Epub 2012 Dec 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23277573 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic release factor 3 is required for multiple turnovers of peptide release catalysis by eukaryotic release factor 1.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 11;288(41):29530-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.487090. Epub 2013 Aug 20. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23963452 Free PMC article.
-
A data-driven estimation of the ribosome drop-off rate in S. cerevisiae reveals a correlation with the genes length.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024 Apr 18;6(2):lqae036. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqae036. eCollection 2024 Jun. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 38638702 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of release factor RF3 with the translation machinery.Mol Genet Genomics. 2015 Aug;290(4):1335-44. doi: 10.1007/s00438-015-0994-x. Epub 2015 Jan 31. Mol Genet Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25636454
References
-
- Adamski FM, McCaughan KK, Jorgensen F, Kurland CG, Tate WP. The concentration of polypeptide chain release factors 1 and 2 at different growth rates of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1994;238:302–308. - PubMed
-
- Andersson DI, Bohman K, Isaksson LA, Kurland CG. Translation rates and misreading characteristics of rpsD mutants in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187:467–472. - PubMed
-
- Capecchi MR, Klein HA. Characterization of three proteins involved in polypeptide chain termination. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:469–477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

