Childhood risk factors predict cardiovascular disease, impaired fasting glucose plus type 2 diabetes mellitus, and high blood pressure 26 years later at a mean age of 38 years: the Princeton-lipid research clinics follow-up study
- PMID: 22001337
- PMCID: PMC3324938
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2011.08.010
Childhood risk factors predict cardiovascular disease, impaired fasting glucose plus type 2 diabetes mellitus, and high blood pressure 26 years later at a mean age of 38 years: the Princeton-lipid research clinics follow-up study
Abstract
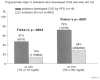
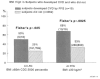
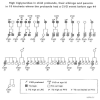
The objective was to assess whether pediatric risk factors predict cardiovascular disease (CVD), impaired fasting glucose (IFG) + type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and high blood pressure (HBP) in young adulthood. We performed a prospective follow-up of 909 public-parochial suburban schoolchildren first studied at ages 6 to 18 years and 26 years later at a mean age of 38 years. Pediatric triglycerides (TGs), blood pressure, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, body mass index, and glucose above and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol below established pediatric cutoffs, along with race, cigarette smoking, family history of CVD, T2DM, and HBP, were assessed as determinants of young adult CVD, a composite variable including IFG + T2DM and HBP. By stepwise logistic regression, adult CVD (19 yes, 862 no) was associated with pediatric high TG (odds ratio [OR], 5.85; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.3-14.7). High TG in pediatric probands with young adult CVD was familial and was associated with early CVD in their high-TG parents. Adult IFG + T2DM (114 yes, 535 no) was associated with parental T2DM (OR, 2.2; 95% CI, 1.38-3.6), high childhood glucose (OR, 4.43; 95% CI, 2-9.7), and childhood cigarette smoking (OR, 1.64; 95% CI, 1.03-2.61). Adult HBP (133 yes, 475 no) was associated with pediatric high body mass index (OR, 2.7; 95% CI, 1.7-4.3) and HBP (OR, 2.5; 95% CI, 1.5-4.3). Pediatric risk factors are significantly, independently related to young adult CVD, IFG + T2DM, and HBP. Identification of pediatric risk factors for CVD, IFG + T2DM, and HBP facilitates initiation of primary prevention programs to reduce development of adult CVD, IFG + T2DM, and HBP.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
The child as proband for future parental cardiometabolic disease: the 26-year prospective Princeton Lipid Research Clinics Follow-up Study.J Pediatr. 2012 Apr;160(4):590-597.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2011.12.003. Epub 2012 Jan 13. J Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 22244461 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes retained from childhood to adulthood predict adult outcomes: the Princeton LRC Follow-up Study.Int J Pediatr Endocrinol. 2012 Apr 16;2012(1):6. doi: 10.1186/1687-9856-2012-6. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22507454 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric triglycerides predict cardiovascular disease events in the fourth to fifth decade of life.Metabolism. 2009 Sep;58(9):1277-84. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2009.04.009. Epub 2009 Jun 18. Metabolism. 2009. PMID: 19501856 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose--a review of diagnosis, clinical implications and management.Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2005 Feb;2(1):9-15. doi: 10.3132/dvdr.2005.007. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2005. PMID: 16305067 Review.
-
Development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in people with intermediate hyperglycaemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 29;10(10):CD012661. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012661.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30371961 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Childhood BMI and Fasting Glucose and Insulin Predict Adult Type 2 Diabetes: The International Childhood Cardiovascular Cohort (i3C) Consortium.Diabetes Care. 2020 Nov;43(11):2821-2829. doi: 10.2337/dc20-0822. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Diabetes Care. 2020. PMID: 32873588 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Pediatric Obesity on Diurnal Blood Pressure Assessment and Cardiovascular Risk Markers.Front Pediatr. 2021 Mar 4;9:596142. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.596142. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33748038 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Effects of Childhood Risk Factors on Cardiovascular Health During Adulthood.Clin Med Rev Vasc Health. 2015 Aug 12;7:1-5. doi: 10.4137/CMRVH.S29964. Clin Med Rev Vasc Health. 2015. PMID: 26312015 Free PMC article.
-
Adolescent metabolic syndrome and its components associations with incidence of type 2 diabetes in early adulthood: Tehran lipid and glucose study.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021 Jan 2;13(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13098-020-00608-1. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021. PMID: 33388084 Free PMC article.
-
Sociodemographic Correlates of High Cardiovascular Health Across Childhood and Adolescence: A Prospective Study Among 2 Cohorts in the ECHO Consortium.J Am Heart Assoc. 2024 Aug 6;13(15):e036279. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.036279. Epub 2024 Jul 31. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024. PMID: 39082419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Juonala M, Magnussen CG, Venn A, et al. Influence of age on associations between childhood risk factors and carotid intima-media thickness in adulthood: the Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study, the Childhood Determinants of Adult Health Study, the Bogalusa Heart Study, and the Muscatine Study for the International Childhood Cardiovascular Cohort (i3C) Consortium. Circulation. 2010;122:2514–20. - PubMed
-
- Juonala M, Viikari JS, Kahonen M, et al. Life-time risk factors and progression of carotid atherosclerosis in young adults: the Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns study. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:1745–51. - PubMed
-
- Magnussen CG, Venn A, Thomson R, et al. The association of pediatric low- and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol dyslipidemia classifications and change in dyslipidemia status with carotid intima-media thickness in adulthood evidence from the cardiovascular risk in Young Finns study, the Bogalusa Heart study, and the CDAH (Childhood Determinants of Adult Health) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:860–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Freedman DS, Dietz WH, Tang R, et al. The relation of obesity throughout life to carotid intima-media thickness in adulthood: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004;28:159–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

