Blinded study determination of high sensitivity and specificity microchip electrophoresis-SSCP/HA to detect mutations in the p53 gene
- PMID: 22002021
- PMCID: PMC3416029
- DOI: 10.1002/elps.201100396
Blinded study determination of high sensitivity and specificity microchip electrophoresis-SSCP/HA to detect mutations in the p53 gene
Abstract
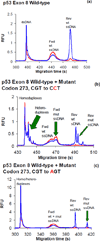
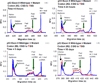
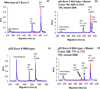
Knowledge of the genetic changes that lead to disease has grown and continues to grow at a rapid pace. However, there is a need for clinical devices that can be used routinely to translate this knowledge into the treatment of patients. Use in a clinical setting requires high sensitivity and specificity (>97%) in order to prevent misdiagnoses. Single-strand conformational polymorphism (SSCP) and heteroduplex analysis (HA) are two DNA-based, complementary methods for mutation detection that are inexpensive and relatively easy to implement. However, both methods are most commonly detected by slab gel electrophoresis, which can be labor-intensive, time-consuming, and often the methods are unable to produce high sensitivity and specificity without the use of multiple analysis conditions. Here, we demonstrate the first blinded study using microchip electrophoresis (ME)-SSCP/HA. We demonstrate the ability of ME-SSCP/HA to detect with 98% sensitivity and specificity >100 samples from the p53 gene exons 5-9 in a blinded study in an analysis time of <10 min.
Copyright © 2011 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no financial or commercial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An optimized microchip electrophoresis system for mutation detection by tandem SSCP and heteroduplex analysis for p53 gene exons 5-9.Electrophoresis. 2006 Oct;27(19):3823-35. doi: 10.1002/elps.200600358. Electrophoresis. 2006. PMID: 16972304
-
Optimized sample preparation for tandem capillary electrophoresis single-stranded conformational polymorphism/ heteroduplex analysis.Biotechniques. 2002 Aug;33(2):318-20, 322, 324-5. doi: 10.2144/02332st04. Biotechniques. 2002. PMID: 12188184
-
High sensitivity of detection of TP53 somatic mutations by fluorescence-assisted mismatch analysis.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2002 Sep;35(1):86-91. doi: 10.1002/gcc.10102. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2002. PMID: 12203794
-
Economical protocol for combined single-strand conformation polymorphism and heteroduplex analysis on a standard capillary electrophoresis apparatus.Methods Mol Biol. 2010;653:181-92. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-759-4_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20721743 Review.
-
Single-strand conformation polymorphism and heteroduplex analysis for gel-based mutation detection.Electrophoresis. 1999 Jun;20(6):1177-85. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1522-2683(19990101)20:6<1177::AID-ELPS1177>3.0.CO;2-2. Electrophoresis. 1999. PMID: 10380757 Review.
Cited by
-
Capillary electrophoresis applied to DNA: determining and harnessing sequence and structure to advance bioanalyses (2009-2014).Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015 Sep;407(23):6923-38. doi: 10.1007/s00216-015-8703-5. Epub 2015 May 3. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25935677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolating single stranded DNA using a microfluidic dialysis device.Analyst. 2014 Jan 7;139(1):215-24. doi: 10.1039/c3an01880f. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Analyst. 2014. PMID: 24213273 Free PMC article.
-
Capillary electrophoresis-single strand conformation polymorphism for the detection of multiple mutations leading to tuberculosis drug resistance.J Microbiol Methods. 2012 Oct;91(1):147-54. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2012.07.021. Epub 2012 Aug 3. J Microbiol Methods. 2012. PMID: 22884688 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Venter J, Adams M, Myers E, Li P, Mural R, Sutton G, Smith H, Yandell M, Evans C, Holt R, et al. Science. 2001;291:1304–1351. - PubMed
-
- Lander E, Linton L, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody M, Baldwin J, Devom K, Dewar K, Doyle M, FitzHugh W, et al. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
-
- Levine A, Momand J, Finlay C. Nature. 1991;351:453–456. - PubMed
-
- Olivier M, Eeles R, Hollstein M, Khan M, Harris C, Hainaut P. Human Mutation. 2002;19:607–614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

