The unfolded protein response (UPR)-activated transcription factor X-box-binding protein 1 (XBP1) induces microRNA-346 expression that targets the human antigen peptide transporter 1 (TAP1) mRNA and governs immune regulatory genes
- PMID: 22002058
- PMCID: PMC3308892
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.304956
The unfolded protein response (UPR)-activated transcription factor X-box-binding protein 1 (XBP1) induces microRNA-346 expression that targets the human antigen peptide transporter 1 (TAP1) mRNA and governs immune regulatory genes
Abstract
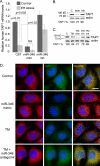
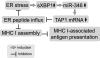
To identify endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-induced microRNAs (miRNA) that govern ER protein influx during the adaptive phase of unfolded protein response, we performed miRNA microarray profiling and analysis in human airway epithelial cells following ER stress induction using proteasome inhibition or tunicamycin treatment. We identified miR-346 as the most significantly induced miRNA by both classic stressors. miR-346 is encoded within an intron of the glutamate receptor ionotropic delta-1 gene (GRID1), but its ER stress-associated expression is independent of GRID1. We demonstrated that the spliced X-box-binding protein-1 (sXBP1) is necessary and sufficient for ER stress-associated miR-346 induction, revealing a novel role for this unfolded protein response-activated transcription factor. In mRNA profiling arrays, we identified 21 mRNAs that were reduced by both ER stress and miR-346. The target genes of miR-346 regulate immune responses and include the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I gene products, interferon-induced genes, and the ER antigen peptide transporter 1 (TAP1). Although most of the repressed mRNAs appear to be indirect targets because they lack specific seeding sites for miR-346, we demonstrate that the human TAP1 mRNA is a direct target of miR-346. The human TAP1 mRNA 3'-UTR contains a 6-mer canonical seeding site for miR-346. Importantly, the ER stress-associated reduction in human TAP1 mRNA and protein levels could be reversed with an miR-346 antagomir. Because TAP function is necessary for proper MHC class I-associated antigen presentation, our results provide a novel mechanistic explanation for reduced MHC class I-associated antigen presentation that was observed during ER stress.
Figures


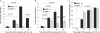


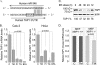
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

