The RAD9-RAD1-HUS1 (9.1.1) complex interacts with WRN and is crucial to regulate its response to replication fork stalling
- PMID: 22002307
- PMCID: PMC3272477
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.468
The RAD9-RAD1-HUS1 (9.1.1) complex interacts with WRN and is crucial to regulate its response to replication fork stalling
Abstract
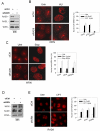
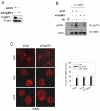
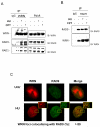
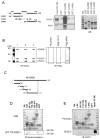
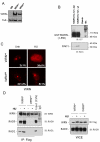
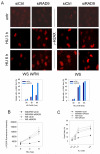
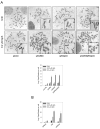
The WRN protein belongs to the RecQ family of DNA helicases and is implicated in replication fork restart, but how its function is regulated remains unknown. We show that WRN interacts with the 9.1.1 complex, one of the central factors of the replication checkpoint. This interaction is mediated by the binding of the RAD1 subunit to the N-terminal region of WRN and is instrumental for WRN relocalization in nuclear foci and its phosphorylation in response to replication arrest. We also find that ATR-dependent WRN phosphorylation depends on TopBP1, which is recruited by the 9.1.1 complex in response to replication arrest. Finally, we provide evidence for a cooperation between WRN and 9.1.1 complex in preventing accumulation of DNA breakage and maintaining genome integrity at naturally occurring replication fork stalling sites. Taken together, our data unveil a novel functional interplay between WRN helicase and the replication checkpoint, contributing to shed light into the molecular mechanism underlying the response to replication fork arrest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
ATR and ATM differently regulate WRN to prevent DSBs at stalled replication forks and promote replication fork recovery.EMBO J. 2010 Sep 15;29(18):3156-69. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.205. Epub 2010 Aug 27. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20802463 Free PMC article.
-
The Werner syndrome protein: linking the replication checkpoint response to genome stability.Aging (Albany NY). 2011 Mar;3(3):311-8. doi: 10.18632/aging.100293. Aging (Albany NY). 2011. PMID: 21389352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WRN helicase regulates the ATR-CHK1-induced S-phase checkpoint pathway in response to topoisomerase-I-DNA covalent complexes.J Cell Sci. 2011 Dec 1;124(Pt 23):3967-79. doi: 10.1242/jcs.081372. Epub 2011 Dec 8. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 22159421 Free PMC article.
-
Werner syndrome protein participates in a complex with RAD51, RAD54, RAD54B and ATR in response to ICL-induced replication arrest.J Cell Sci. 2006 Dec 15;119(Pt 24):5137-46. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03291. Epub 2006 Nov 21. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 17118963
-
Interplay between wrn and the checkpoint in s-phase.Ital J Biochem. 2007 Jun;56(2):130-40. Ital J Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17722654 Review.
Cited by
-
Conditional inactivation of the DNA damage response gene Hus1 in mouse testis reveals separable roles for components of the RAD9-RAD1-HUS1 complex in meiotic chromosome maintenance.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(2):e1003320. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003320. Epub 2013 Feb 28. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23468651 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation by CK2 regulates MUS81/EME1 in mitosis and after replication stress.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jun 1;46(10):5109-5124. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky280. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29850896 Free PMC article.
-
RecQ DNA Helicase Rqh1 Promotes Rad3ATR Kinase Signaling in the DNA Replication Checkpoint Pathway of Fission Yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Aug 14;40(17):e00145-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00145-20. Print 2020 Aug 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32541066 Free PMC article.
-
Checkpoint-dependent and independent roles of the Werner syndrome protein in preserving genome integrity in response to mild replication stress.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Nov 10;42(20):12628-39. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1022. Epub 2014 Oct 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25352544 Free PMC article.
-
Human RecQ helicases in DNA repair, recombination, and replication.Annu Rev Biochem. 2014;83:519-52. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060713-035428. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Annu Rev Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24606147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bao S, Lu T, Wang X, Zheng H, Wang LE, Wei Q, et al. Disruption of the Rad9/Rad1/Hus1 (9-1-1) complex leads to checkpoint signaling and replication defects. Oncogene. 2004;23:5586–5593. - PubMed
-
- Blander G, Zalle N, Daniely Y, Taplick J, Gray MD, Oren M. DNA damage-induced translocation of the Werner helicase is regulated by acetylation. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:50934–50940. - PubMed
-
- Brosh RM, Jr., Waheed J, Sommers JA. Biochemical characterization of the DNA substrate specificity of Werner syndrome helicase. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:23236–23245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

