Prostaglandin E2 EP receptors as therapeutic targets in breast cancer
- PMID: 22002714
- PMCID: PMC3640271
- DOI: 10.1007/s10555-011-9303-2
Prostaglandin E2 EP receptors as therapeutic targets in breast cancer
Abstract
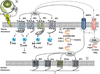
Prostaglandins are lipid compounds that mediate many physiological effects. Prostaglandin E2 (PGE(2)) is the most abundant prostanoid in the human body, and synthesis of PGE(2) is driven by cyclooxygenase enzymes including COX-2. Both elevated expression of COX-2 and increased PGE(2) levels have been associated with many cancers including breast cancer. PGE(2) exerts its effect by binding to the E series of prostaglandin receptors (EP) which are G protein-coupled receptors. Four EP receptor subtypes exist, EP1-4, and each is coupled to different intracellular signaling pathways. As downstream effectors of the COX-2 pathway, EP receptors have been shown to play a role in breast and other malignancies and in cancer metastasis. The role of each EP receptor in malignant behavior is complex and involves the interplay of EP receptor signaling on the tumor cell, on stromal cells, and on host immune effector cells. While preclinical and epidemiological data support the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and selective COX-2 inhibitors (COXibs) for the prevention and treatment of malignancy, toxicities due to COXibs as well as less than promising results from clinical trials have laboratories seeking alternative targets. As knowledge concerning the role of EP receptors in cancer grows, so does the potential for exploiting EP receptors as therapeutic targets for the treatment or prevention of cancer and cancer metastasis.
Figures
References
-
- Legler DF, Bruckner M, Uetz-von Allmen E, Krause P. Prostaglandin E2 at new glance: novel insights in functional diversity offer therapeutic chances. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010;42(2):198–201. - PubMed
-
- Wang M-T, Honn KV, Nie D. Cyclooxygenases, prostanoids, and tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26(3–4):525–534. - PubMed
-
- Sugimoto Y, Narumiya S. Prostaglandin E receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282(16):11613–11617. - PubMed
-
- Dannenberg AJ, Subbaramaiah K. Targeting cyclooxygenase-2 in human neoplasia: rationale and promise. Cancer Cell. 2003;4(6):431–436. - PubMed
-
- Kundu N, Yang Q, Dorsey R, Fulton AM. Increased cyclooxygenase-2 (cox-2) expression and activity in a murine model of metastatic breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer. 2001;93(5):681–686. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

