Serum paraoxonase-3 concentration in HIV-infected patients. Evidence for a protective role against oxidation
- PMID: 22003209
- PMCID: PMC3243473
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.P018457
Serum paraoxonase-3 concentration in HIV-infected patients. Evidence for a protective role against oxidation
Abstract
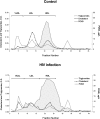
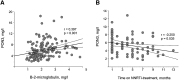
We investigated the influence of the HIV infection on serum paraoxonase-3 (PON3) concentration and assessed the relationships with lipoprotein-associated abnormalities, immunological response, and accelerated atherosclerosis. We studied 207 HIV-infected patients and 385 healthy volunteers. Serum PON3 was determined by in-house ELISA, and PON3 distribution in lipoproteins was investigated by fast-performance liquid chromatography (FPLC). Polymorphisms of the PON3 promoter were analyzed by the Iplex Gold MassArray(TM) method. PON3 concentrations were increased (about three times) in HIV-infected patients with respect to controls (P < 0.001) and were inversely correlated with oxidized LDL levels (P = 0.038). Long-term use of nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI)-based antiretroviral therapy was associated with a decrease of PON3 concentrations. In a multivariate linear regression analysis, these relationships were still strong when the main confounding covariates were considered. PON3 was mainly found in HDL in HIV-infected patients, but a substantial amount of the protein was detected in LDL particles. This study reports for the first time an important increase in serum PON3 concentrations in HIV-infected patients that is associated with their oxidative status and their treatment with NNRTI. Long-term, prospective studies are needed to confirm the possible influence of this enzyme on the course of this disease and its possible utility as an analytical biomarker.
Figures

References
-
- Boyd M., Reiss P. 2006. The long-term consequences of antiretroviral therapy: a review. J. HIV Ther. 11: 26–35. - PubMed
-
- Bergersen B. M. 2006. Cardiovascular risk in patients with HIV infection: impact of antiretroviral therapy. Drugs. 66: 1971–1987. - PubMed
-
- Rose H., Woolley I., Hoy J., Dart A., Bryant B., Mijch A., Sviridov D. 2006. HIV infection and high-density lipoprotein: the effect of disease vs. the effect of treatment. Metabolism. 55: 90–95. - PubMed
-
- Alonso-Villaverde C., Segués T., Coll-Crespo B., Pérez-Bernalte R., Rabassa A., Gomila M., Parra S., Gozález-Esteban M. A., Jiménez-Expósito M. J., Masana L. 2003. High-density lipoprotein concentrations relate to the clinical course of HIV viral load in patients undergoing antiretroviral therapy. AIDS. 17: 1173–1178. - PubMed
-
- Parra S., Alonso-Villaverde C., Coll B., Ferré N., Marsillach J., Aragonès G., Mackness M., Mackness B., Masana L., Joven J., et al. 2007. Serum paraoxonase-1 activity and concentration are influenced by human immunodeficiency virus infection. Atherosclerosis. 194: 175–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

