Lipopolysaccharide enhances transforming growth factor β1-induced platelet-derived growth factor-B expression in bile duct epithelial cells
- PMID: 22004089
- PMCID: PMC3262076
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06941.x
Lipopolysaccharide enhances transforming growth factor β1-induced platelet-derived growth factor-B expression in bile duct epithelial cells
Abstract
Background and aim: Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-B is a potent profibrogenic mediator expressed by bile duct epithelial cells (BDECs) that contributes to liver fibrosis after bile duct ligation. However, the mechanism of PDGF-B induction in BDECs during cholestasis is not known. Transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) also contribute to the profibrogenic response after bile duct ligation. We tested the hypothesis that LPS and TGFβ1 synergistically induce PDGF-B expression in BDECs.
Methods: Transformed human BDECs (MMNK-1 cells) and primary rat BDECs were stimulated with LPS and/or TGFβ1, and signaling pathways through which LPS potentiates TGFβ1-induced PDGF-B mRNA expression were investigated.
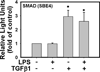
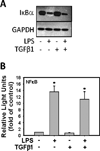
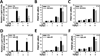
Results: Stimulation of MMNK-1 cells with LPS alone did not significantly induce PDGF-B mRNA expression. However, LPS co-treatment enhanced TGFβ1 induction of PDGF-B mRNA in MMNK-1 cells and also in primary rat BDECs. Importantly, co-treatment of MMNK-1 cells with LPS and TGFβ1 also significantly increased PDGF-BB protein expression. Interestingly, LPS did not affect TGFβ1 activation of a SMAD-dependent reporter construct. Rather, stimulation of MMNK-1 cells with LPS, but not TGFβ1, increased JNK1/2 phosphorylation. Expression of dominant negative JNK2, but not dominant negative JNK1, inhibited the LPS potentiation of TGFβ1-induced PDGF-B mRNA expression in MMNK-1 cells. In addition, LPS treatment caused IκBα degradation and activation of a nuclear factor κB (NFκB)-dependent reporter construct. Expression of an IκBα super repressor inhibited activation of NFκB and attenuated LPS potentiation of TGFβ1-induced PDGF-B mRNA.
Conclusions: The results indicate that LPS activation of NFκB and JNK2 enhances TGFβ1-induced PDGF-B expression in BDECs.
© 2011 Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Foundation and Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Pierce GF, Mustoe TA, Altrock BW, Deuel TF, Thomason A. Role of platelet-derived growth factor in wound healing. J. Cell Biochem. 1991;45:319–326. - PubMed
-
- Czochra P, Klopcic B, Meyer E, et al. Liver fibrosis induced by hepatic overexpression of PDGF-B in transgenic mice. J. Hepatol. 2006;45:419–428. - PubMed
-
- Isbrucker RA, Peterson TC. Platelet-derived growth factor and pentoxifylline modulation of collagen synthesis in myofibroblasts. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1998;149:120–126. - PubMed
-
- Kinnman N, Francoz C, Barbu V, et al. The myofibroblastic conversion of peribiliary fibrogenic cells distinct from hepatic stellate cells is stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor during liver fibrogenesis. Lab Invest. 2003;83:163–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

