Comprehensive motor testing in Fmr1-KO mice exposes temporal defects in oromotor coordination
- PMID: 22004265
- PMCID: PMC4874324
- DOI: 10.1037/a0025920
Comprehensive motor testing in Fmr1-KO mice exposes temporal defects in oromotor coordination
Abstract
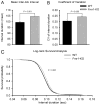
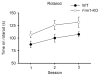
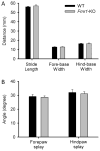
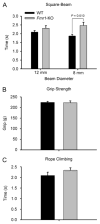
Fragile X syndrome (FXS; MIM #300624), a well-recognized form of inherited human mental retardation is caused, in most cases, by a CGG trinucleotide repeat expansion in the 5'-untranslated region of FMR1, resulting in reduced expression of the fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP). Clinical features include macroorchidism, anxiety, mental retardation, motor coordination, and speech articulation deficits. The Fmr1 knockout (Fmr1-KO) mouse, a mouse model for FXS, has been shown to replicate the macroorchidism, cognitive deficits, and neuroanatomical abnormalities found in human FXS. Here we asked whether Fmr1-KO mice also display appendicular and oromotor deficits comparable to the ataxia and dysarthric speech seen in FXS patients. We employed standard motor tests for balance and appendicular motor coordination, and used a novel long-term fluid-licking assay to investigate oromotor function in Fmr1-KO mice and their wild-type (WT) littermates. Fmr1-KO mice performed equally well as their WT littermates on standard motor tests, with the exception of a raised-beam task. However, Fmr1-KO mice had a significantly slower licking rhythm than their WT littermates. Deficits in rhythmic fluid-licking in Fmr1-KO mice have been linked to cerebellar pathologies. It is believed that balance and motor coordination deficits in FXS patients are caused by cerebellar neurophathologies. The neuronal bases of speech articulation deficits in FXS patients are currently unknown. It is yet to be established whether similar neuronal circuits control rhythmic fluid-licking pattern in mice and speech articulation movement in humans.
PsycINFO Database Record (c) 2011 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Antar LN, Afroz R, Dictenberg JB, Carroll RC, Bassell GJ. Metabotropic glutamate receptor activation regulates fragile X mental retardation protein and FMR1 mRNA localization differentially in dendrites and at synapses. Journal of Neuroscience. 2004;24:2648–2655. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0099-04.2004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

