Genome-wide significant association between alcohol dependence and a variant in the ADH gene cluster
- PMID: 22004471
- PMCID: PMC3245349
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2011.00395.x
Genome-wide significant association between alcohol dependence and a variant in the ADH gene cluster
Abstract
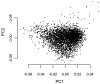
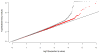
Alcohol dependence (AD) is an important contributory factor to the global burden of disease. The etiology of AD involves both environmental and genetic factors, and the disorder has a heritability of around 50%. The aim of the present study was to identify susceptibility genes for AD by performing a genome-wide association study (GWAS). The sample comprised 1333 male in-patients with severe AD according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edition, and 2168 controls. These included 487 patients and 1358 controls from a previous GWAS study by our group. All individuals were of German descent. Single-marker tests and a polygenic score-based analysis to assess the combined contribution of multiple markers with small effects were performed. The single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs1789891, which is located between the ADH1B and ADH1C genes, achieved genome-wide significance [P = 1.27E-8, odds ratio (OR) = 1.46]. Other markers from this region were also associated with AD, and conditional analyses indicated that these made a partially independent contribution. The SNP rs1789891 is in complete linkage disequilibrium with the functional Arg272Gln variant (P = 1.24E-7, OR = 1.31) of the ADH1C gene, which has been reported to modify the rate of ethanol oxidation to acetaldehyde in vitro. A polygenic score-based approach produced a significant result (P = 9.66E-9). This is the first GWAS of AD to provide genome-wide significant support for the role of the ADH gene cluster and to suggest a polygenic component to the etiology of AD. The latter result may indicate that many more AD susceptibility genes still await identification.
© 2011 The Authors, Addiction Biology © 2011 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures


References
-
- Ball D. Addiction science and its genetics. Addiction. 2008;103:360–367. - PubMed
-
- Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics. 2004;21:263–265. - PubMed
-
- Bierut LJ, Agrawal A, Bucholz KK, Doheny KF, Laurie C, Pugh E, Fisher S, Fox L, Howells W, Bertelsen S, Hinrichs AL, Almasy L, Breslau N, Culverhouse RC, Dick DM, Edenberg HJ, Foroud T, Grucza RA, Hatsukami D, Hesselbrock V, Johnson EO, Kramer J, Krueger RF, Kuperman S, Lynskey M, Mann K, Neuman RJ, Nöthen MM, Nurnberger JI, Porjesz B, Ridinger M, Saccone NL, Saccone SF, Schuckit MA, Tischfield JA, Wang JC, Rietschel M, Goate AM, Rice JP. A genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:5082–5087. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA089392/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004422/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA013423/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 5 R01 AA013320-04/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH087590/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U10 AA008401/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AA011998-11/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA013320/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U10AA008401/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AA011998/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA011998/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG004422/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH081862/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200782096C/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

