Risk factors for late renal dysfunction after pediatric heart transplantation: a multi-institutional study
- PMID: 22004544
- PMCID: PMC3201752
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-3046.2011.01564.x
Risk factors for late renal dysfunction after pediatric heart transplantation: a multi-institutional study
Abstract
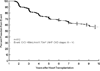
Renal dysfunction is a major determinant of outcome after HTx. Using a large, multi-institutional database, we sought to identify factors associated with late renal dysfunction after pediatric HTx. All patients in the PHTS database with eGFR ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m(2) at one yr post-HTx (n = 812) were analyzed by Cox regression for association with risk factors for eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m(2) at >1 yr after HTx. Freedom from late renal dysfunction was 71% and 57% at five and 10 yr. Multivariate risk factors for late renal dysfunction were earlier era of HTx (HR 1.84; p < 0.001), black race (HR 1.42; p = 0.048), rejection with hemodynamic compromise in the first year after HTx (HR 1.74; p = 0.038), and lowest quartile eGFR at one yr post-HTx (HR 1.83; p < 0.001). Renal function at HTx was not associated with onset of late renal dysfunction. Eleven patients (1.4%) required chronic dialysis and/or renal transplant during median follow-up of 4.1 yr (1.5-12.6). Late renal dysfunction is common after pediatric HTx, with blacks at increased risk. Decreased eGFR at one yr post-HTx, but not at HTx, predicts onset of late renal dysfunction. Future research on strategies to minimize late renal dysfunction after pediatric HTx may be of greatest benefit if focused on these subgroups.
© 2011 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Conflict of interest statement
No author has a financial interest or other potential conflict of interest related to subject matter or materials mentioned in the manuscript.
Figures
Comment in
-
Monitoring and improving renal outcomes after heart transplantation.Pediatr Transplant. 2011 Nov;15(7):665-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3046.2011.01573.x. Epub 2011 Sep 5. Pediatr Transplant. 2011. PMID: 21895904 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ojo AO, Held PJ, Port FK, et al. Chronic renal failure after transplantation of a nonrenal organ. N Engl J Med. 2003 Sep 4;349(10):931–940. - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson AH, Cohen DJ. Renal failure in the recipients of nonrenal solid organ transplants. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999 May;10(5):1136–1144. - PubMed
-
- Filler G, Sharma AP. High prevalence of chronic kidney disease in pediatric solid organ transplantation. Pediatr Transplant. 2009 Feb;13(1):7–10. - PubMed
-
- Lee CK, Christensen LL, Magee JC, Ojo AO, Harmon WE, Bridges ND. Pre-transplant risk factors for chronic renal dysfunction after pediatric heart transplantation: A 10-year national cohort study. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2007 May;26(5):458–465. - PubMed
-
- Ader JL, Rostaing L. Cyclosporin nephrotoxicity: Pathophysiology and comparison with FK-506. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 1998 Sep;7(5):539–545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous