The new low-toxic histone deacetylase inhibitor S-(2) induces apoptosis in various acute myeloid leukaemia cells
- PMID: 22004558
- PMCID: PMC3822689
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01464.x
The new low-toxic histone deacetylase inhibitor S-(2) induces apoptosis in various acute myeloid leukaemia cells
Erratum in
-
Correction to "The new low-toxic histone deacetylase inhibitor S-(2) induces apoptosis in various acute myeloid leukaemia cells".J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Nov;28(21):e70001. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70001. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39513549 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
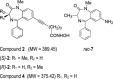
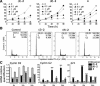
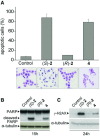
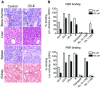
Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) induce tumour cell cycle arrest and/or apoptosis, and some of them are currently used in cancer therapy. Recently, we described a series of powerful HDACi characterized by a 1,4-benzodiazepine (BDZ) ring hybridized with a linear alkyl chain bearing a hydroxamate function as Zn(++)--chelating group. Here, we explored the anti-leukaemic properties of three novel hybrids, namely the chiral compounds (S)-2 and (R)-2, and their non-chiral analogue 4, which were first comparatively tested in promyelocytic NB4 cells. (S)-2 and partially 4--but not (R)-2--caused G0/G1 cell-cycle arrest by up-regulating cyclin G2 and p21 expression and down-regulating cyclin D2 expression, and also apoptosis as assessed by cell morphology and cytofluorimetric assay, histone H2AX phosphorylation and PARP cleavage. Notably, these events were partly prevented by an anti-oxidant. Moreover, novel HDACi prompted p53 and α-tubulin acetylation and, consistently, inhibited HDAC1 and 6 activity. The rank order of potency was (S)-2 > 4 > (R)-2, reflecting that of other biological assays and addressing (S)-2 as the most effective compound capable of triggering apoptosis in various acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) cell lines and blasts from patients with different AML subtypes. Importantly, (S)-2 was safe in mice (up to 150 mg/kg/week) as determined by liver, spleen, kidney and bone marrow histopathology; and displayed negligible affinity for peripheral/central BDZ-receptors. Overall, the BDZ-hydroxamate (S)-2 showed to be a low-toxic HDACi with powerful anti-proliferative and pro-apototic activities towards different cultured and primary AML cells, and therefore of clinical interest to support conventional anti-leukaemic therapy.
© 2012 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2012 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of the histone deacetylase inhibitor (S)-2 against LNCaP and PC3 human prostate cancer cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58267. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058267. Epub 2013 Mar 4. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23469273 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of 1,2-benzisoxazole tethered 1,2,3-triazoles that exhibit anticancer activity in acute myeloid leukemia cell lines by inhibiting histone deacetylases, and inducing p21 and tubulin acetylation.Bioorg Med Chem. 2015 Sep 15;23(18):6157-65. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.07.069. Epub 2015 Aug 1. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26299825
-
Design, synthesis and evaluation of antiproliferative activity of melanoma-targeted histone deacetylase inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017 Feb 15;27(4):744-749. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.01.044. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017. PMID: 28131715 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor induces cell apoptosis and cycle arrest in lung cancer cells via mitochondrial injury and p53 up-acetylation.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2016 Dec;32(6):469-482. doi: 10.1007/s10565-016-9347-8. Epub 2016 Jul 16. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27423454 Free PMC article.
-
Novel hydroxamate and anilide derivatives as potent histone deacetylase inhibitors: synthesis and antiproliferative evaluation.Curr Med Chem. 2003 Nov;10(22):2359-72. doi: 10.2174/0929867033456585. Curr Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 14529479 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of anesthetic drugs in liver apoptosis.Hepat Mon. 2013 Aug 25;13(8):e13162. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.13162. Hepat Mon. 2013. PMID: 24069040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining the role of histone deacetylases in the inhibition of mammary carcinogenesis by dietary energy restriction (DER): effects of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) and DER in a rat model.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013 Apr;6(4):290-8. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-12-0449-T. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013. PMID: 23365133 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC1 controls CIP2A transcription in human colorectal cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 May 3;7(18):25862-71. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8406. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27029072 Free PMC article.
-
Improved HDAC Inhibition, Stronger Cytotoxic Effect and Higher Selectivity against Leukemias and Lymphomas of Novel, Tricyclic Vorinostat Analogues.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Aug 26;14(9):851. doi: 10.3390/ph14090851. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34577551 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a Novel Indolocarbazole as Histone Deacetylases Inhibitor against Leukemia Cell Lines.J Anal Methods Chem. 2015;2015:675053. doi: 10.1155/2015/675053. Epub 2015 Nov 16. J Anal Methods Chem. 2015. PMID: 26649226 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marks P, Rifkind RA, Richon VM, et al. Histone deacetylases and cancer: causes and therapies. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001;1:194–202. - PubMed
-
- Kouzarides T. Histone acetylases and deacetylases in cell proliferation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999;9:40–8. - PubMed
-
- Monneret C. Histone deacetylase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 2005;40:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW. Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:769–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

