Identification of novel Bartonella spp. in bats and evidence of Asian gray shrew as a new potential reservoir of Bartonella
- PMID: 22005177
- PMCID: PMC7126237
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.09.031
Identification of novel Bartonella spp. in bats and evidence of Asian gray shrew as a new potential reservoir of Bartonella
Abstract
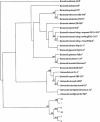
Many studies indicated that small mammals are important reservoirs for Bartonella species. Using molecular methods, several studies have documented that bats could harbor Bartonella. This study was conducted to investigate the relationship of Bartonella spp. identified in bats and small mammals living in the same ecological environment. During May 2009 and March 2010, a total of 102 blood specimens were collected. By whole blood culture and molecular identification, a total of 6 bats, 1 rodent and 9 shrews were shown to be infected by Bartonella species. After sequencing and phylogenetic analyses of the sequences of gltA, ftsZ, rpoB and ribC genes, these specific isolates from bats were not similar to the known Bartonella species (the similarity values were less than 91.2%, 90.5%, 88.8%, and 82.2%, respectively); these isolates formed an independent clade away from other known Bartonella type strains. The Bartonella spp. isolated from small mammals, which were closely related to Bartonella tribocorum, Bartonella elizabethae, Bartonella grahamii, Bartonella rattimassiliensis and Bartonella queenslandensis, were similar to the findings in previous studies worldwide. Therefore, the results implied that the species of Bartonella strains isolated from small mammals were different from those identified in bats. Our results strongly suggested that the bat isolate could be a new Bartonella species. This study is also the first one to isolate Bartonella organisms from Asian gray shrews, Crocidura attenuata tanakae.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epidemiology of Bartonella infection in rodents and shrews in Taiwan.Zoonoses Public Health. 2010 Sep;57(6):439-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1863-2378.2009.01234.x. Zoonoses Public Health. 2010. PMID: 19538457
-
Prevalence of zoonotic Bartonella species among rodents and shrews in Thailand.Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014 Mar;37(2):109-14. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24393304
-
Bartonella species in small mammals and their ectoparasites in Taiwan.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010 Oct;83(4):917-23. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.10-0083. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010. PMID: 20889892 Free PMC article.
-
Bartonella DNA in heart tissues of bats in central and eastern Europe and a review of phylogenetic relations of bat-associated bartonellae.Parasit Vectors. 2018 Aug 29;11(1):489. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-3070-7. Parasit Vectors. 2018. PMID: 30157912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular phylogeny of the genus Bartonella: what is the current knowledge?FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001 Jun 12;200(1):1-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10684.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001. PMID: 11410341 Review.
Cited by
-
Bartonella spp. in fruit bats and blood-feeding Ectoparasites in Madagascar.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015 Feb 23;9(2):e0003532. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003532. eCollection 2015 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015. PMID: 25706653 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum DNA in the lesser horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus hipposideros) guano.Epidemiol Infect. 2018 Jul;146(10):1253-1258. doi: 10.1017/S0950268818001279. Epub 2018 May 30. Epidemiol Infect. 2018. PMID: 29843834 Free PMC article.
-
White-Toothed Shrews (Genus Crocidura): Potential Reservoirs for Zoonotic Leptospira spp. and Arthropod-Borne Pathogens?Pathogens. 2023 May 30;12(6):781. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12060781. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37375471 Free PMC article.
-
Bats and their ectoparasites (Nycteribiidae and Spinturnicidae) carry diverse novel Bartonella genotypes, China.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2022 Jul;69(4):e845-e858. doi: 10.1111/tbed.14357. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2022. PMID: 34695291 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and genetic properties of Bartonella in eastern bent-wing bats (Miniopterus fuliginosus) in Japan.Infect Genet Evol. 2020 Sep;83:104354. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104354. Epub 2020 May 5. Infect Genet Evol. 2020. PMID: 32380314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai Y., Kosoy M.Y., Lerdthusnee K., Peruski L.F., Richardson J.H. Prevalence and genetic heterogeneity of Bartonella strains cultured from rodents from 17 provinces in Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009;81:811–816. - PubMed
-
- Bai Y., Kosoy M.Y., Boonmar S., Sawatwong P., Sangmaneedet S., Peruski L.F. Enrichment culture and molecular identification of diverse Bartonella species in stray dogs. Vet. Microbiol. 2010;146:314–319. - PubMed
-
- Bermond D., Heller R., Barrat F., Delacour G., Dehio C., Alliot A., Monteil H., Chomel B., Boulouis H.J., Piemont Y. Bartonella birtlesii sp. nov., isolated from small mammals (Apodemus spp.) Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000;50:1973–1979. - PubMed
-
- Bermond D., Boulouis H.J., Heller R., Van Laere G., Monteil H., Chomel B.B., Sander A., Dehio C., Piemont Y. Bartonella bovis sp. nov. and Bartonella capreoli sp. nov., isolated from European ruminants. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002;52:383–390. - PubMed
-
- Birtles R.J., Harrison T.G., Saunders N.A., Molyneux D.H. Proposals to unify the genera Grahamella and Bartonella, with descriptions of Bartonella talpae comb. nov., Bartonella peromysci comb. nov., and three new species, Bartonella grahamii sp. nov., Bartonella taylorii sp. nov., and Bartonella doshiae sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1995;45:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

