FoxO4 inhibits atherosclerosis through its function in bone marrow derived cells
- PMID: 22005198
- PMCID: PMC3226872
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.09.038
FoxO4 inhibits atherosclerosis through its function in bone marrow derived cells
Abstract
Objectives: FoxO proteins are transcription factors involved in varieties of cellular processes, including immune cell homeostasis, cytokine production, anti-oxidative stress, and cell proliferation and differentiation. Although these processes are implicated in the development of atherosclerosis, very little is known about the role of FoxO proteins in the context of atherosclerosis. Our objectives were to determine whether and how inactivation of Foxo4, a member of the FoxO family, in vivo promotes atherosclerosis.
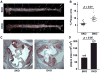
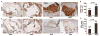
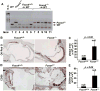
Methods and results: Apolipoprotein E-deficient (apoE(-/-)) mice were crossbred with animals lacking Foxo4 (Foxo4(-/-)). After 10 weeks on a high fat diet (HFD), Foxo4(-/-)apoE(-/-) mice showed elevated atherosclerosis and increased amount of macrophages and T cells in the plaque compared to apoE(-/-) mice. Bone marrow transplantations of chimeric C57B/6 mice reconstituted with either wild-type or Foxo4(-/-) bone marrows indicate that Foxo4-deficiency in bone marrow derived cells sufficiently promoted atherosclerosis. Foxo4-null macrophages produced elevated inflammatory cytokine IL-6 and levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in response to lipopolysaccharides in vitro. Serum levels of IL-6 were upregulated in HFD-fed Foxo4(-/-)apoE(-/-) mice compared to those of apoE(-/-) mice.
Conclusions: FoxO4 inhibits atherosclerosis through bone marrow derived cells, possibly by inhibition of ROS and inflammatory cytokines that promote monocyte recruitment and/or retention.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- Andersson J, Libby P, Hansson GK. Adaptive immunity and atherosclerosis. Clin Immunol. 2010;134:33–46. - PubMed
-
- Ando H, Tsuruoka S, Yamamoto H, Takamura T, Kaneko S, Fujimura A. Regulation of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase mRNA expression in C57BL/6 mice fed an atherogenic diet. Atherosclerosis. 2005;178:265–269. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio-Vergara M, Shiri-Sverdlov R, de Haan G, Hofker MH. Bone marrow transplantation in mice as a tool for studying the role of hematopoietic cells in metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Atherosclerosis. 2010 [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Baglione J, Smith JD. Quantitative assay for mouse atherosclerosis in the aortic root. Methods Mol Med. 2006;129:83–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

