Blockade of acid sensing ion channels attenuates the augmented exercise pressor reflex in rats with chronic femoral artery occlusion
- PMID: 22005681
- PMCID: PMC3286694
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.217851
Blockade of acid sensing ion channels attenuates the augmented exercise pressor reflex in rats with chronic femoral artery occlusion
Abstract
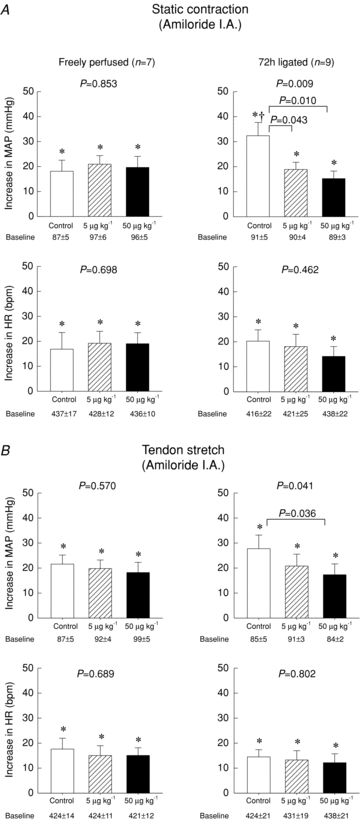
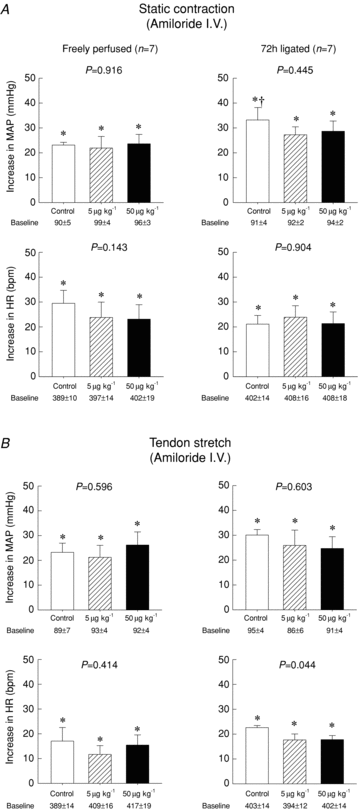
We found previously that static contraction of the hindlimb muscles of rats whose femoral artery was ligated evoked a larger reflex pressor response (i.e. exercise pressor reflex) than did static contraction of the contralateral hindlimb muscles which were freely perfused. Ligating a femoral artery in rats results in blood flow patterns to the muscles that are remarkably similar to those displayed by humans with peripheral artery disease. Using decerebrated rats, we tested the hypothesis that the augmented exercise pressor reflex in rats with a ligated femoral artery is attenuated by blockade of the acid sensing ion channel (ASIC) 3. We found that femoral arterial injection of either amiloride (5 and 50 μg kg(-1)) or APETx2 (100 μg kg(-1)) markedly attenuated the reflex in rats with a ligated femoral artery. In contrast, these ASIC antagonists had only modest effects on the reflex in rats with freely perfused hindlimbs. Tests of specificity of the two antagonists revealed that the low dose of amiloride and APETx2 greatly attenuated the pressor response to lactic acid, an ASIC agonist, but did not attenuate the pressor response to capsaicin, a TRPV1 agonist. In contrast, the high dose of amiloride attenuated the pressor responses to lactic acid, but also attenuated the pressor response to capsaicin. We conclude that ASIC3 on thin fibre muscle afferents plays an important role in evoking the exercise pressor reflex in rats with a compromised arterial blood supply to the working muscles.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Chronic femoral artery occlusion augments exercise pressor reflex in decerebrated rats.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Jul;299(1):H106-13. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00141.2010. Epub 2010 Apr 23. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20418475 Free PMC article.
-
Combined, but not individual, blockade of ASIC3, P2X, and EP4 receptors attenuates the exercise pressor reflex in rats with freely perfused hindlimb muscles.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015 Dec 1;119(11):1330-6. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00630.2015. Epub 2015 Oct 15. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015. PMID: 26472871 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle pressor reflex: potential role of vanilloid type 1 receptor and acid-sensing ion channel.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2004 Nov;97(5):1709-14. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00389.2004. Epub 2004 Jun 25. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2004. PMID: 15220301
-
Dorsal root tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels do not contribute to the augmented exercise pressor reflex in rats with chronic femoral artery occlusion.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Feb;300(2):H652-63. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00859.2010. Epub 2010 Nov 12. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21076028 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanosensitive channels in the mechanical component of the exercise pressor reflex.Auton Neurosci. 2023 Dec;250:103128. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2023.103128. Epub 2023 Oct 29. Auton Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37925831 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined effect of acid-sensing ion channel 3 and transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 gene polymorphisms on blood pressure variations in Taiwanese.Tzu Chi Med J. 2018 Jan-Mar;30(1):29-36. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_187_17. Tzu Chi Med J. 2018. PMID: 29643714 Free PMC article.
-
Functional knockout of the TRPV1 channel has no effect on the exercise pressor reflex in rats.J Physiol. 2023 Dec;601(23):5241-5256. doi: 10.1113/JP285267. Epub 2023 Oct 25. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37878364 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral µ-opioid receptors attenuate the responses of group III and IV afferents to contraction in rats with simulated peripheral artery disease.J Neurophysiol. 2018 Jun 1;119(6):2052-2058. doi: 10.1152/jn.00034.2018. Epub 2018 Feb 21. J Neurophysiol. 2018. PMID: 29465323 Free PMC article.
-
ASIC3 contributes to the blunted muscle metaboreflex in heart failure.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015 Feb;47(2):257-63. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000000415. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015. PMID: 24983337 Free PMC article.
-
The mechano-gated channel inhibitor GsMTx4 reduces the exercise pressor reflex in rats with ligated femoral arteries.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016 May 1;310(9):H1233-41. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00974.2015. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26921442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baccelli G, Reggiani P, Mattioli A, Corbellini E, Garducci S, Catalano M. The exercise pressor reflex and changes in radial arterial pressure and heart rate during walking in patients with arteriosclerosis obliterans. Angiology. 1999;50:361–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

