Basilar artery aneurysm at a persistent trigeminal artery junction. A case report and literature review
- PMID: 22005697
- PMCID: PMC3396038
- DOI: 10.1177/159101991101700310
Basilar artery aneurysm at a persistent trigeminal artery junction. A case report and literature review
Abstract
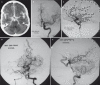
The trigeminal artery is an anastomosis between the embryonic precursors of the vertebrobasilar and carotid systems, and may persist into adult life. The association of the persistent primitive trigeminal artery (PTA) with cerebral aneurysm is well documented in the literature and, in general, aneurysms are located in the anterior circulation. We describe a patient who presented with a panencephalic Fisher III subarachnoid hemorrhage due to rupture of an intracranial aneurysm. Digital arteriography showed a saccular aneurysm in the middle third of the basilar artery, adjacent to the junction with a persistent trigeminal artery. She was submitted to endovascular treatment with embolization of the basilar artery aneurysm with coils. Aneurysms at the PTA junction with the basilar artery are rare. This paper describes a case of PTA associated with an aneurysm in the basilar artery at PTA junction and briefly reviews the literature.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[The persistent trigeminal artery in vascular brain diseases].Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko. 1998 Apr-Jun;(2):3-6. Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko. 1998. PMID: 9720157 Russian.
-
Medial type persistent trigeminal artery associated with a saccular aneurysm at its trunk.Surg Radiol Anat. 2021 Mar;43(3):433-436. doi: 10.1007/s00276-020-02656-8. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Surg Radiol Anat. 2021. PMID: 33427924
-
Fusiform aneurysm of a persistent trigeminal artery associated with rare intracranial arterial variations and subarachnoid hemorrhage.Surg Radiol Anat. 2015 Jan;37(1):115-8. doi: 10.1007/s00276-014-1304-8. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Surg Radiol Anat. 2015. PMID: 25053265
-
Primitive persistent carotid-basilar and carotid-vertebral anastomoses: a report of seven cases and a review of the literature.Clin Anat. 1995;8(1):36-43. doi: 10.1002/ca.980080107. Clin Anat. 1995. PMID: 7697511 Review.
-
Persistent primitive trigeminal artery associated with a cavernous carotid aneurysm. Case report and literature review.J Radiol Case Rep. 2018 Nov 30;12(11):1-11. doi: 10.3941/jrcr.v12i11.3500. eCollection 2018 Nov. J Radiol Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 30647831 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ruptured Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery Aneurysm From a Persistent Trigeminal Artery: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 May 20;16(5):e60648. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60648. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38903290 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomical insights and clinical implications of the persistent trigeminal artery: A cadaveric study utilizing latex injection techniques.Surg Neurol Int. 2025 Mar 28;16:103. doi: 10.25259/SNI_1084_2024. eCollection 2025. Surg Neurol Int. 2025. PMID: 40206769 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential aneurysms with incidental persistent primitive trigeminal artery: Is this association purely coincidental? A case study and review of the literature in search for a pathobiological mechanism.Surg Neurol Int. 2022 Nov 4;13:508. doi: 10.25259/SNI_828_2022. eCollection 2022. Surg Neurol Int. 2022. PMID: 36447855 Free PMC article.
-
Rupture of Persistent Primitive Trigeminal Artery-basilar Artery Aneurysm Managed with Stent-assisted Coiling.Asian J Neurosurg. 2018 Jul-Sep;13(3):817-821. doi: 10.4103/ajns.AJNS_53_16. Asian J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30283555 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple aneurysms, aortic coarctation, and persistent trigeminal artery. A unique presentation.Surg Neurol Int. 2019 Jan 18;10:6. doi: 10.4103/sni.sni_395_18. eCollection 2019. Surg Neurol Int. 2019. PMID: 30775060 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ali S, Radaideh MM, Shaibani A, et al. Persistent trigeminal artery terminating in the posterior inferior cerebellar artery: case report. Neurosurgery. 2008;62:746–748 . - PubMed
-
- Varghese SPJ. Persistent trigeminal artery and associated vascular variations. Australasian Radiology. 2007;51:31–33 . - PubMed
-
- Cloft HJ, Razack N, Kallmes DF, et al. Prevalence of cerebral aneurysms in patients with persistent primitive trigeminal artery. J Neurosurg. 1999;90:865–867 . - PubMed
-
- Takase T, Tanabe H, Kondo A, et al. Surgically treated aneurysm of the trunk of the persistent primitive trigeminal artery-case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2004;44:420–423 . - PubMed
-
- Padget DH. The development of the cranial arteries in the human embryo. Contrib Embryol. 1948;32:205–262 .
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

