Comparative performance of cell life span and cell transit models for describing erythropoietic drug effects
- PMID: 22005901
- PMCID: PMC3231865
- DOI: 10.1208/s12248-011-9302-9
Comparative performance of cell life span and cell transit models for describing erythropoietic drug effects
Abstract
Prolonged time delay in response to drug action is a common feature of hematological responses to pharmacotherapy such as erythropoiesis. The objective of this study was to compare the performance of two competing modeling approaches for delayed drug effects, mechanistic cell life span models, and semi-mechanistic cell transit models. The comparison was performed with an experimental dataset from multiple dose administrations of an erythropoietin mimetic to Cynomolgus monkeys. Comparative performance measures include visual predictive checks, goodness-of-fit plots, model estimation time, estimation status, and estimation error. The analysis revealed that both models resulted in a similarly good description of the erythropoietic drug effect, with precision and bias of the model-based predictions of red blood cell counts of less than 11%. The cell transit model needed slightly longer time to converge compared to the cell life span model. The system and drug effect parameters were similar in both models indicating that the models can be interchangeably used to describe the current data. Thus, model selection would be dependent on the purpose of the modeling exercise, the available data, and the time allocated for model development.
Figures
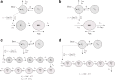
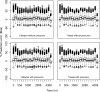
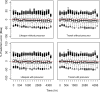
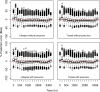
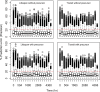
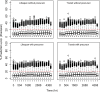
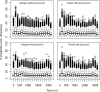
References
-
- Sheiner LB, Stanski DR, Vozeh S, Miller RD, Ham J. Simultaneous modeling of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: application to d-tubocurarine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979;25:358–371. - PubMed
-
- Loeffler M, Pantel K, Wulff H, Wichmann HE. A mathematical model of erythropoiesis in mice and rats. Part 1: structure of the model. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1989;22:13–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

