Alarming levels of drug-resistant tuberculosis in Belarus: results of a survey in Minsk
- PMID: 22005924
- PMCID: PMC3393766
- DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00145411
Alarming levels of drug-resistant tuberculosis in Belarus: results of a survey in Minsk
Abstract
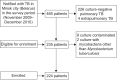
Resistance to anti-tuberculosis (TB) medicines is a major public health threat in most countries of the former Soviet Union. As no representative and quality-assured information on the magnitude of this problem existed in Belarus, a survey was conducted in the capital city of Minsk. Between November 2009 and December 2010, 156 consecutively diagnosed new and 68 previously treated culture-positive TB patients residing in Minsk were enrolled in the survey. Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates were obtained from each patient and tested for susceptibility to first- and second-line anti-TB drugs. Multidrug-resistant (MDR)-TB was found in 35.3% (95% CI 27.7-42.8) of new patients and 76.5% (95% CI 66.1-86.8) of those previously treated. Overall, nearly one in two patients enrolled had MDR-TB. Extensively drug-resistant TB was reported in 15 of the 107 MDR-TB patients (14.0%, 95% CI 7.3-20.7). Patients <35 yrs of age have shown a two times higher odds ratio of multidrug-resistant TB than those aged >35 yrs. The findings of this survey in Minsk city are alarming and represent the highest proportions of MDR-TB ever recorded in the world. This study greatly contributes to the understanding of the burden of drug-resistant TB in urban areas of Belarus.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Comment in
-
Re-think first-line tuberculosis treatment.Eur Respir J. 2013 Feb;41(2):488-9. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00112612. Eur Respir J. 2013. PMID: 23370809 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kliiman K, Altraja A. Predictors of poor treatment outcome in multi- and extensively drug-resistant pulmonary TB. Eur Respir J 2009; 33: 1085–1094 - PubMed
-
- Leimane V, Dravniece G, Riekstina V, et al. Treatment outcome of multidrug/extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in Latvia, 2000–2004. Eur Respir J 2010; 36: 584–593 - PubMed
-
- Migliori GB, Sotgiu G, Lange C, et al. Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis: back to the future. Eur Respir J 2010; 36: 475–477 - PubMed
-
- Migliori GB, Besozzi G, Girardi E, et al. Clinical and operational value of the extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis definition. Eur Respir J 2007; 30: 623–626 - PubMed
-
- Sotgiu G, Ferrara G, Matteelli A, et al. Epidemiology and clinical management of XDR-TB: a systematic review by TBNET. Eur Respir J 2009; 33: 871–881 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials