β-arrestin2 plays permissive roles in the inhibitory activities of RGS9-2 on G protein-coupled receptors by maintaining RGS9-2 in the open conformation
- PMID: 22006018
- PMCID: PMC3233032
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.05690-11
β-arrestin2 plays permissive roles in the inhibitory activities of RGS9-2 on G protein-coupled receptors by maintaining RGS9-2 in the open conformation
Abstract
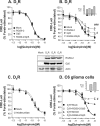
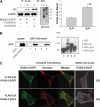
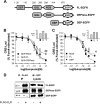
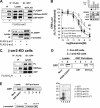
Together with G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) kinases (GRKs) and β-arrestins, RGS proteins are the major family of molecules that control the signaling of GPCRs. The expression pattern of one of these RGS family members, RGS9-2, coincides with that of the dopamine D(3) receptor (D(3)R) in the brain, and in vivo studies have shown that RGS9-2 regulates the signaling of D2-like receptors. In this study, β-arrestin2 was found to be required for scaffolding of the intricate interactions among the dishevelled-EGL10-pleckstrin (DEP) domain of RGS9-2, Gβ5, R7-binding protein (R7BP), and D(3)R. The DEP domain of RGS9-2, under the permission of β-arrestin2, inhibited the signaling of D(3)R in collaboration with Gβ5. β-Arrestin2 competed with R7BP and Gβ5 so that RGS9-2 is placed in the cytosolic region in an open conformation which is able to inhibit the signaling of GPCRs. The affinity of the receptor protein for β-arrestin2 was a critical factor that determined the selectivity of RGS9-2 for the receptor it regulates. These results show that β-arrestins function not only as mediators of receptor-G protein uncoupling and initiators of receptor endocytosis but also as scaffolding proteins that control and coordinate the inhibitory effects of RGS proteins on the signaling of certain GPCRs.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Macromolecular composition dictates receptor and G protein selectivity of regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) 7 and 9-2 protein complexes in living cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 30;288(35):25129-25142. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.462283. Epub 2013 Jul 15. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23857581 Free PMC article.
-
The membrane anchor R7BP controls the proteolytic stability of the striatal specific RGS protein, RGS9-2.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 16;282(7):4772-4781. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M610518200. Epub 2006 Dec 7. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17158100
-
Type 5 G protein beta subunit (Gbeta5) controls the interaction of regulator of G protein signaling 9 (RGS9) with membrane anchors.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 17;286(24):21806-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.241513. Epub 2011 Apr 21. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21511947 Free PMC article.
-
β-Arrestins and G protein-coupled receptor trafficking.Methods Enzymol. 2013;521:91-108. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-391862-8.00005-3. Methods Enzymol. 2013. PMID: 23351735 Review.
-
Phosphorylation barcoding as a mechanism of directing GPCR signaling.Sci Signal. 2011 Aug 9;4(185):pe36. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002331. Sci Signal. 2011. PMID: 21868354 Review.
Cited by
-
Moderate Alcohol Exposure during the Rat Equivalent to the Third Trimester of Human Pregnancy Alters Regulation of GABAA Receptor-Mediated Synaptic Transmission by Dopamine in the Basolateral Amygdala.Front Pediatr. 2014 May 27;2:46. doi: 10.3389/fped.2014.00046. eCollection 2014. Front Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 24904907 Free PMC article.
-
Novel roles for β-arrestins in the regulation of pharmacological sequestration to predict agonist-induced desensitization of dopamine D3 receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Nov;170(5):1112-29. doi: 10.1111/bph.12357. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23992580 Free PMC article.
-
RGS2 modulates the activity and internalization of dopamine D2 receptors in neuroblastoma N2A cells.Neuropharmacology. 2016 Nov;110(Pt A):297-307. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.08.009. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 27528587 Free PMC article.
-
RGS9-2 rescues dopamine D2 receptor levels and signaling in DYT1 dystonia mouse models.EMBO Mol Med. 2019 Jan;11(1):e9283. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201809283. EMBO Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30552094 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Regulation of Dopamine D₃ Receptor through Interaction with PICK1.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2016 Sep 1;24(5):475-81. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2016.015. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2016. PMID: 27169823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballon D. R., et al. 2006. DEP domain-mediated regulation of GPCR signaling responses. Cell 126:1079–1093 - PubMed
-
- Beom S., Cheong D., Torres G., Caron M. G., Kim K. M. 2004. Comparative studies of molecular mechanisms of dopamine D2 and D3 receptors for the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 279:28304–28314 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
