A soluble α-synuclein construct forms a dynamic tetramer
- PMID: 22006323
- PMCID: PMC3203798
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1113260108
A soluble α-synuclein construct forms a dynamic tetramer
Abstract
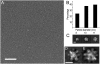
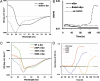
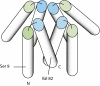
A heterologously expressed form of the human Parkinson disease-associated protein α-synuclein with a 10-residue N-terminal extension is shown to form a stable tetramer in the absence of lipid bilayers or micelles. Sequential NMR assignments, intramonomer nuclear Overhauser effects, and circular dichroism spectra are consistent with transient formation of α-helices in the first 100 N-terminal residues of the 140-residue α-synuclein sequence. Total phosphorus analysis indicates that phospholipids are not associated with the tetramer as isolated, and chemical cross-linking experiments confirm that the tetramer is the highest-order oligomer present at NMR sample concentrations. Image reconstruction from electron micrographs indicates that a symmetric oligomer is present, with three- or fourfold symmetry. Thermal unfolding experiments indicate that a hydrophobic core is present in the tetramer. A dynamic model for the tetramer structure is proposed, based on expected close association of the amphipathic central helices observed in the previously described micelle-associated "hairpin" structure of α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Goedert M. Alpha-synuclein and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:492–501. - PubMed
-
- Jellinger KA. Neuropathological spectrum of synucleinopathies. Mov Disord. 2003;18(Suppl 6):S2–S12. - PubMed
-
- Klockgether T. Parkinson's disease: Clinical aspects. Cell Tissue Res. 2004;318(1):115–120. - PubMed
-
- George JM, Jin H, Woods WS, Clayton DF. Characterization of a novel protein regulated during the critical period for song learning in the zebra finch. Neuron. 1995;15:361–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

