Dual farnesoid X receptor/TGR5 agonist INT-767 reduces liver injury in the Mdr2-/- (Abcb4-/-) mouse cholangiopathy model by promoting biliary HCO⁻₃ output
- PMID: 22006858
- PMCID: PMC3744065
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.24537
Dual farnesoid X receptor/TGR5 agonist INT-767 reduces liver injury in the Mdr2-/- (Abcb4-/-) mouse cholangiopathy model by promoting biliary HCO⁻₃ output
Abstract
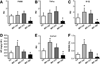
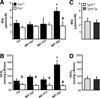
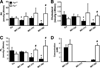
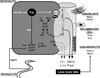
Chronic cholangiopathies have limited therapeutic options and represent an important indication for liver transplantation. The nuclear farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and the membrane G protein-coupled receptor, TGR5, regulate bile acid (BA) homeostasis and inflammation. Therefore, we hypothesized that activation of FXR and/or TGR5 could ameliorate liver injury in Mdr2(-/-) (Abcb4(-/-)) mice, a model of chronic cholangiopathy. Hepatic inflammation, fibrosis, as well as bile secretion and key genes of BA homeostasis were addressed in Mdr2(-/-) mice fed either a chow diet or a diet supplemented with the FXR agonist, INT-747, the TGR5 agonist, INT-777, or the dual FXR/TGR5 agonist, INT-767 (0.03% w/w). Only the dual FXR/TGR5 agonist, INT-767, significantly improved serum liver enzymes, hepatic inflammation, and biliary fibrosis in Mdr2(-/-) mice, whereas INT-747 and INT-777 had no hepatoprotective effects. In line with this, INT-767 significantly induced bile flow and biliary HCO 3- output, as well as gene expression of carbonic anhydrase 14, an important enzyme able to enhance HCO 3- transport, in an Fxr-dependent manner. In addition, INT-767 dramatically reduced bile acid synthesis via the induction of ileal Fgf15 and hepatic Shp gene expression, thus resulting in significantly reduced biliary bile acid output in Mdr2(-/-) mice.
Conclusion: This study shows that FXR activation improves liver injury in a mouse model of chronic cholangiopathy by reduction of biliary BA output and promotion of HCO 3--rich bile secretion.
Copyright © 2011 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: Dr. Adornini owns stock in Intercept. Dr. Trauner is a consultant for Phenex. He is on the speakers’ bureau of Falk and received grants from Intercept.
Figures


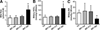

References
-
- Ishibashi H, Komori A, Shimoda S, Gershwin ME. Guidelines for therapy of autoimmune liver disease. Semin Liver Dis. 2007;27:214–226. - PubMed
-
- Lazaridis KN, Strazzabosco M, Larusso NF. The cholangiopathies: disorders of biliary epithelia. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1565–1577. - PubMed
-
- Makishima M, Okamoto AY, Repa JJ, Tu H, Learned RM, Luk A, et al. Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science. 1999;284:1362–1365. - PubMed
-
- Parks DJ, Blanchard SG, Bledsoe RK, Chandra G, Consler TG, Kliewer SA, et al. Bile acids: natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor. Science. 1999;284:1365–1368. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Chen J, Hollister K, Sowers LC, Forman BM. Endogenous bile acids are ligands for the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR. Mol Cell. 1999;3:543–553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
