Distinct docking mechanisms mediate interactions between the Msg5 phosphatase and mating or cell integrity mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 22006927
- PMCID: PMC3234975
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.286948
Distinct docking mechanisms mediate interactions between the Msg5 phosphatase and mating or cell integrity mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
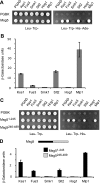
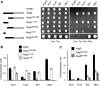
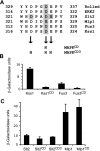
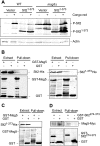
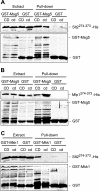
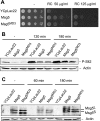
MAPK phosphatases (MKPs) are negative regulators of signaling pathways with distinct MAPK substrate specificities. For example, the yeast dual specificity phosphatase Msg5 dephosphorylates the Fus3 and Slt2 MAPKs operating in the mating and cell wall integrity pathways, respectively. Like other MAPK-interacting proteins, most MKPs bind MAPKs through specific docking domains. These include D-motifs, which contain basic residues that interact with acidic residues in the common docking (CD) domain of MAPKs. Here we show that Msg5 interacts not only with Fus3, Kss1, and Slt2 but also with the pseudokinase Slt2 paralog Mlp1. Using yeast two-hybrid and in vitro interaction assays, we have identified distinct regions within the N-terminal domain of Msg5 that differentially bind either the MAPKs Fus3 and Kss1 or Slt2 and Mlp1. Whereas a canonical D-site within Msg5 mediates interaction with the CD domains of Fus3 and Kss1, a novel motif ((102)IYT(104)) within Msg5 is involved in binding to Slt2 and Mlp1. Furthermore, mutation of this site prevents the phosphorylation of Msg5 by Slt2. This motif is conserved in Sdp1, another MKP that dephosphorylates Slt2, as well as in Msg5 orthologs from other yeast species. A region spanning amino acids 274-373 within Slt2 and Mlp1 mediates binding to this Msg5 motif in a CD domain-independent manner. In contrast, Slt2 uses its CD domain to bind to its upstream activator Mkk1. This binding flexibility may allow MAPK pathways to exploit additional regulatory controls in order to provide fine modulation of both pathway activity and specificity.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

