Identification of extremely premature infants at high risk of rehospitalization
- PMID: 22007016
- PMCID: PMC3208965
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2011-1142
Identification of extremely premature infants at high risk of rehospitalization
Abstract
Objective: Extremely low birth weight infants often require rehospitalization during infancy. Our objective was to identify at the time of discharge which extremely low birth weight infants are at higher risk for rehospitalization.
Methods: Data from extremely low birth weight infants in Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network centers from 2002-2005 were analyzed. The primary outcome was rehospitalization by the 18- to 22-month follow-up, and secondary outcome was rehospitalization for respiratory causes in the first year. Using variables and odds ratios identified by stepwise logistic regression, scoring systems were developed with scores proportional to odds ratios. Classification and regression-tree analysis was performed by recursive partitioning and automatic selection of optimal cutoff points of variables.
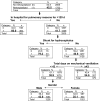
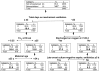
Results: A total of 3787 infants were evaluated (mean ± SD birth weight: 787 ± 136 g; gestational age: 26 ± 2 weeks; 48% male, 42% black). Forty-five percent of the infants were rehospitalized by 18 to 22 months; 14.7% were rehospitalized for respiratory causes in the first year. Both regression models (area under the curve: 0.63) and classification and regression-tree models (mean misclassification rate: 40%-42%) were moderately accurate. Predictors for the primary outcome by regression were shunt surgery for hydrocephalus, hospital stay of >120 days for pulmonary reasons, necrotizing enterocolitis stage II or higher or spontaneous gastrointestinal perforation, higher fraction of inspired oxygen at 36 weeks, and male gender. By classification and regression-tree analysis, infants with hospital stays of >120 days for pulmonary reasons had a 66% rehospitalization rate compared with 42% without such a stay.
Conclusions: The scoring systems and classification and regression-tree analysis models identified infants at higher risk of rehospitalization and might assist planning for care after discharge.
Figures
References
-
- deRegnier RA, Roberts D, Ramsey D, Weaver RG, Jr, O'Shea TM. Association between the severity of chronic lung disease and first-year outcomes of very low birth weight infants. J Perinatol. 1997;17(5):375–382 - PubMed
-
- Furman L, Baley J, Borawski-Clark E, Aucott S, Hack M. Hospitalization as a measure of morbidity among very low birth weight infants with chronic lung disease. J Pediatr. 1996;128(4):447–452 - PubMed
-
- Lamarche-Vadel A, Blondel B, Truffer P, et al. Re-hospitalization in infants younger than 29 weeks' gestation in the EPIPAGE cohort. Acta Paediatr. 2004;93(10):1340–1345 - PubMed
-
- Underwood MA, Danielsen B, Gilbert WM. Cost, causes and rates of rehospitalization of preterm infants. J Perinatol. 2007;27(10):614–619 - PubMed
-
- Korvenranta E, Lehtonen L, Peltola M, et al. Morbidities and hospital resource use during the first 3 years of life among very preterm infants. Pediatrics. 2009;124(1):128–134 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U10 HD27851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HD054420/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40521/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR633/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR24149/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR024149/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR24160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006022/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR44/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR6022/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD34216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR70/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD36790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040521/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR008084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR125/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040461/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR7122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR24148/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40461/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR39/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR30/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024148/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR007122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR80/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR16587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR750/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR8084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR32/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD036790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR24139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States

