Apoplastic reactive oxygen species transiently decrease auxin signaling and cause stress-induced morphogenic response in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 22007024
- PMCID: PMC3327221
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.111.181883
Apoplastic reactive oxygen species transiently decrease auxin signaling and cause stress-induced morphogenic response in Arabidopsis
Abstract
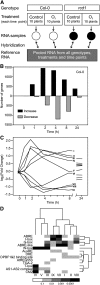
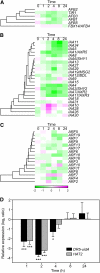
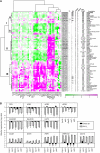
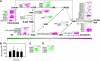
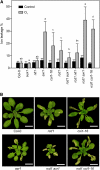
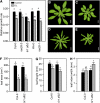
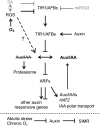
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are ubiquitous signaling molecules in plant stress and development. To gain further insight into the plant transcriptional response to apoplastic ROS, the phytotoxic atmospheric pollutant ozone was used as a model ROS inducer in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) and gene expression was analyzed with microarrays. In contrast to the increase in signaling via the stress hormones salicylic acid, abscisic acid, jasmonic acid (JA), and ethylene, ROS treatment caused auxin signaling to be transiently suppressed, which was confirmed with a DR5-uidA auxin reporter construct. Transcriptomic data revealed that various aspects of auxin homeostasis and signaling were modified by apoplastic ROS. Furthermore, a detailed analysis of auxin signaling showed that transcripts of several auxin receptors and Auxin/Indole-3-Acetic Acid (Aux/IAA) transcriptional repressors were reduced in response to apoplastic ROS. The ROS-derived changes in the expression of auxin signaling genes partially overlapped with abiotic stress, pathogen responses, and salicylic acid signaling. Several mechanisms known to suppress auxin signaling during biotic stress were excluded, indicating that ROS regulated auxin responses via a novel mechanism. Using mutants defective in various auxin (axr1, nit1, aux1, tir1 afb2, iaa28-1, iaa28-2) and JA (axr1, coi1-16) responses, ROS-induced cell death was found to be regulated by JA but not by auxin. Chronic ROS treatment resulted in altered leaf morphology, a stress response known as "stress-induced morphogenic response." Altered leaf shape of tir1 afb2 suggests that auxin was a negative regulator of stress-induced morphogenic response in the rosette.
Figures
References
-
- Ahlfors R, Brosché M, Kollist H, Kangasjärvi J. (2009) Nitric oxide modulates ozone-induced cell death, hormone biosynthesis and gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 58: 1–12 - PubMed
-
- Bretz F, Hothorn T, Westfall T. (2010) Multiple Comparisons Using R. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
-
- Brosché M, Merilo E, Mayer F, Pechter P, Puzõrjova I, Brader G, Kangasjärvi J, Kollist H. (2010) Natural variation in ozone sensitivity among Arabidopsis thaliana accessions and its relation to stomatal conductance. Plant Cell Environ 33: 914–925 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

