Efficient protein transduction method using cationic peptides and lipids
- PMID: 22007148
- PMCID: PMC3189636
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/872065
Efficient protein transduction method using cationic peptides and lipids
Abstract
Cationic peptides termed protein transduction domains (PTDs) have been shown to cross biological membranes efficiently. However, proteins transduced by PTDs become entrapped within the endosomal vesicles and are not delivered into organelles. We have developed a novel protein delivery system to enhance the proton sponge effect, which results in rupture of the endosomes, by using a mixture of Wr-T transporter peptide and a commercially available cationic lipid reagent. This peptide and cationic lipid reagent mixture efficiently delivers a variety of cargo proteins into living cells by releasing them from the endosomes.
Figures
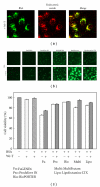

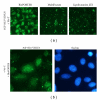
References
-
- Nagahara H, Vocero-Akbani AM, Snyder EL, et al. Transduction of full-length TAT fusion proteins into mammalian cells: TAT-p27(Kip1) induces cell migration. Nature Medicine. 1998;4(12):1449–1452. - PubMed
-
- Derossi D, Joliot AH, Chassaing G, Prochiantz A. The third helix of the Antennapedia homeodomain translocates through biological membranes. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1994;269(14):10444–10450. - PubMed
-
- Fretz M, Jin J, Conibere R, et al. Effects of Na+/H+ exchanger inhibitors on subcellular localisation of endocytic organelles and intracellular dynamics of protein transduction domains HIV-TAT peptide and octaarginine. Journal of Controlled Release. 2006;116(2):247–254. - PubMed
-
- Wadia JS, Stan RV, Dowdy SF. Transducible TAT-HA fusogenic peptide enhances escape of TAT-fusion proteins after lipid raft macropinocytosis. Nature Medicine. 2004;10(3):310–315. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

