Asbestos induces reduction of tumor immunity
- PMID: 22007251
- PMCID: PMC3189469
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/481439
Asbestos induces reduction of tumor immunity
Abstract
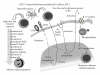
Asbestos-related cancers such as malignant mesothelioma and lung cancer are an important issue in the world. There are many conflicts concerning economical considerations and medical evidence for these cancers and much confusion regarding details of the pathological mechanisms of asbestos-induced cancers. For example, there is uncertainty concerning the degree of danger of the iron-absent chrysotile compared with iron-containing crocidolite and amosite. However, regarding bad prognosis of mesothelioma, medical approaches to ensure the recognition of the biological effects of asbestos and the pathological mechanisms of asbestos-induced carcinogenesis, as well as clinical trials to detect the early stage of mesothelioma, should result in better preventions and the cure of these malignancies. We have been investigating the immunological effects of asbestos in relation to the reduction of tumor immunity. In this paper, cellular and molecular approaches to clarify the immunological effects of asbestos are described, and all the findings indicate that the reduction of tumor immunity is caused by asbestos exposure and involvement in asbestos-induced cancers. These investigations may not only allow the clear recognition of the biological effects of asbestos, but also present a novel procedure for early detection of previous asbestos exposure and the presence of mesothelioma as well as the chemoprevention of asbestos-related cancers.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Search for biomarkers of asbestos exposure and asbestos-induced cancers in investigations of the immunological effects of asbestos.Environ Health Prev Med. 2017 Jun 9;22(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12199-017-0661-4. Environ Health Prev Med. 2017. PMID: 29165150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update of potency factors for asbestos-related lung cancer and mesothelioma.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2008;38 Suppl 1:1-47. doi: 10.1080/10408440802276167. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18671157
-
Estimating the asbestos-related lung cancer burden from mesothelioma mortality.Br J Cancer. 2012 Jan 31;106(3):575-84. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.563. Epub 2012 Jan 10. Br J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22233924 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation profiling of asbestos-treated MeT5A cell line reveals novel pathways implicated in asbestos response.Arch Toxicol. 2018 May;92(5):1785-1795. doi: 10.1007/s00204-018-2179-y. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Arch Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29523930
-
Dysregulation of the immune system caused by silica and asbestos.J Immunotoxicol. 2010 Oct-Dec;7(4):268-78. doi: 10.3109/1547691X.2010.512579. Epub 2010 Sep 20. J Immunotoxicol. 2010. PMID: 20849352 Review.
Cited by
-
Amphibole, but not chrysotile, asbestos induces anti-nuclear autoantibodies and IL-17 in C57BL/6 mice.J Immunotoxicol. 2014 Jul-Sep;11(3):283-90. doi: 10.3109/1547691X.2013.847510. Epub 2013 Oct 28. J Immunotoxicol. 2014. PMID: 24164284 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated cell cycle progression of human regulatory T cell-like cell line caused by continuous exposure to asbestos fibers.Int J Oncol. 2017 Jan;50(1):66-74. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3776. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27878235 Free PMC article.
-
CTLA4 blockade in mesothelioma: finally a competing strategy over cytotoxic/target therapy?Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2015 Jan;64(1):105-12. doi: 10.1007/s00262-014-1609-9. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2015. PMID: 25233793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Search for biomarkers of asbestos exposure and asbestos-induced cancers in investigations of the immunological effects of asbestos.Environ Health Prev Med. 2017 Jun 9;22(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12199-017-0661-4. Environ Health Prev Med. 2017. PMID: 29165150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Asbestos Fibers on Human T Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 23;21(19):6987. doi: 10.3390/ijms21196987. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32977478 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asbestos scandal. Nature. 2010;468(7326):868 pages. - PubMed
-
- Kumagai S, Kurumatani N. Mapping the risk of mesothelioma due to neighborhood asbestos exposure. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2008;178(6):624–629. - PubMed
-
- Kumagai S, Kurumatani N. Asbestos fiber concentration in the area surrounding a former asbestos cement plant and excess mesothelioma deaths in residents. American Journal of Industrial Medicine. 2009;52(10):790–798. - PubMed
-
- Kumagai S, Kurumatani N, Tsuda T, Yorifuji T, Suzuki E. Increased risk of lung cancer mortality among residents near an asbestos product manufacturing plant. International Journal of Occupational and Environmental Health. 2010;16(3):268–278. - PubMed
-
- Yamanaka T, Tanaka F, Hasegawa S, et al. A feasibility study of induction pemetrexed plus cisplatin followed by extrapleural pneumonectomy and postoperative hemithoracic radiation for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2009;39(3):186–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

