Antiatherogenic and Anti-Ischemic Properties of Traditional Chinese Medicine Xinkeshu via Endothelial Protecting Function
- PMID: 22007259
- PMCID: PMC3191825
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/302137
Antiatherogenic and Anti-Ischemic Properties of Traditional Chinese Medicine Xinkeshu via Endothelial Protecting Function
Abstract
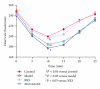
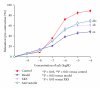
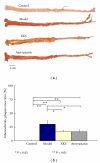
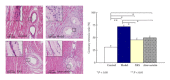
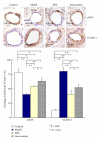
Including herbal medicine, complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) is popular worldwide. The traditional Chinese medicine xinkeshu has been widely used to treat coronary heart disease in China. This study was designed to investigate the protective effect and probable mechanism of xinkeshu tablet to atherosclerotic myocardial ischemia rabbit. Rabbits were divided into four groups (n = 12 each) and fed with different diet for 12 weeks: Control (standard diet), Model (high-cholesterol diet), XKS (high-cholesterol diet with 184.8 mg/kg/d xinkeshu), and Atorvastatin (high-cholesterol diet with 5.0 mg/kg/d atorvastatin). Plasma lipoprotein, ECG, endothelium-dependent vessel relaxation, histomorphological study, and expressions of eNOS and VCAM-1 on coronary arteries were assessed. The findings showed that, similar to atorvastatin, xinkeshu presented significant effects on rescuing endothelium-dependent vessel relaxation, inhibiting atherosclerotic progress, preventing myocardial ischemia, and changing eNOS and VCAM-1 expression. However, xinkeshu showed no lipoprotein lowering effect in hypercholesterolemia rabbits. The results of the present study indicated that xinkeshu exerted potent antiatherogenic and anti-ischemic properties on atherosclerotic myocardial ischemia rabbit. An endothelial protecting effect may be involved in the mechanism other than antihyperlipidemic effect.
Figures

References
-
- Toshima SI, Hasegawa A, Kurabayashi M, et al. Circulating oxidized low density lipoprotein levels. A biochemical risk marker for coronary heart disease. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2000;20(10):2243–2247. - PubMed
-
- Insull W. The pathology of atherosclerosis: plaque development and plaque responses to medical treatment. American Journal of Medicine. 2009;122(supplement 1):S3–S14. - PubMed
-
- Gutterman DD. Silent myocardial ischemia. Circulation Journal. 2009;73(5):785–797. - PubMed
-
- Blum A, Costello R, Samsel L, et al. Variability of C-reactive protein levels among patients with stable coronary artery disease and on statin therapy. Israel Medical Association Journal. 2009;11(10):602–605. - PubMed
-
- Yamashita S, Tsubakio-Yamamoto K, Ohama T, Nakagawa-Toyama Y, Nishida M. Molecular mechanisms of HDL-cholesterol elevation by statins and its effects on HDL functions. Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis. 2010;17(5):436–451. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

