Challenges associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy for metastatic thyroid cancer
- PMID: 22007339
- PMCID: PMC3189619
- DOI: 10.4061/2011/985780
Challenges associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy for metastatic thyroid cancer
Abstract
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) which target angiogenesis are promising treatments for patients with metastatic medullary and differentiated thyroid cancers. Sorafenib, sunitinib, and pazopanib are commercially available drugs which have been studied in these diseases. Vandetanib is the first drug approved in the United States for treatment of medullary thyroid cancer. These TKIs are used as chronic therapies, and therefore it is imperative to understand the adverse event profile in order to avoid excessive toxicity and maintain patients on therapy as long as it proves beneficial. Here we review common toxicities, management of these, and other challenging situations that arise when using TKIs in patients with thyroid cancer.
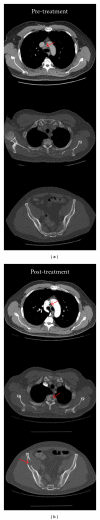
Figures

References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures. American Cancer Society; 2010.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

