Crystal structure-based virtual screening for fragment-like ligands of the human histamine H(1) receptor
- PMID: 22007643
- PMCID: PMC3228891
- DOI: 10.1021/jm2011589
Crystal structure-based virtual screening for fragment-like ligands of the human histamine H(1) receptor
Abstract
The recent crystal structure determinations of druggable class A G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have opened up excellent opportunities in structure-based ligand discovery for this pharmaceutically important protein family. We have developed and validated a customized structure-based virtual fragment screening protocol against the recently determined human histamine H(1) receptor (H(1)R) crystal structure. The method combines molecular docking simulations with a protein-ligand interaction fingerprint (IFP) scoring method. The optimized in silico screening approach was successfully applied to identify a chemically diverse set of novel fragment-like (≤22 heavy atoms) H(1)R ligands with an exceptionally high hit rate of 73%. Of the 26 tested fragments, 19 compounds had affinities ranging from 10 μM to 6 nM. The current study shows the potential of in silico screening against GPCR crystal structures to explore novel, fragment-like GPCR ligand space.
Figures

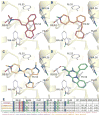


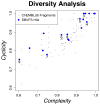
References
-
- Lagerstrom MC, Schioth HB. Structural diversity of G protein-coupled receptors and significance for drug discovery. Nature reviews Drug discovery. 2008;7:339–357. - PubMed
-
- Topiol S, Sabio M. X-ray structure breakthroughs in the GPCR transmembrane region. Biochemical pharmacology. 2009;78:11–20. - PubMed
-
- de Graaf C, Rognan D. Customizing G Protein-coupled receptor models for structure-based virtual screening. Current pharmaceutical design. 2009;15:4026–4048. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

