Bone Morphogenetic Protein functions as a context-dependent angiogenic cue in vertebrates
- PMID: 22008724
- PMCID: PMC3548572
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.10.005
Bone Morphogenetic Protein functions as a context-dependent angiogenic cue in vertebrates
Abstract
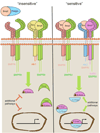
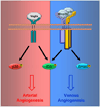
Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) signaling has been implicated in diverse biological processes. Although how BMP signaling regulates behaviors of endothelial cells during angiogenesis are not fully understood, increasing evidence indicate functions of BMP signaling components are essential in developmental and pathological angiogenesis. Here we review recent advances in delineating the functions of BMP signaling during angiogenesis. In addition, we discuss downstream pathways that transduce BMP signaling in endothelial cells, and factors that modulate BMP signaling response in endothelial cells. Finally, we provide recent insight on how BMP signaling functions as a context dependent angiogenic cue.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Kowanetz M, Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathways: therapeutic perspective. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:5018–5022. - PubMed
-
- Shibuya M, Claesson-Welsh L. Signal transduction by VEGF receptors in regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312:549–560. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y, Massague J. Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell. 2003;113:685–700. - PubMed
-
- Derynck R, Zhang YE. Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature. 2003;425:577–584. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

