Reliability of striatal [¹¹C]raclopride binding in smokers wearing transdermal nicotine patches
- PMID: 22009382
- PMCID: PMC4423542
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-011-1965-z
Reliability of striatal [¹¹C]raclopride binding in smokers wearing transdermal nicotine patches
Abstract
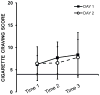
Purpose: In studies where [(11)C]raclopride (RAC) positron emission tomography (PET) is used to assess changes in striatal dopamine, it is important to control for cognitive states, such as drug craving, that could alter dopamine levels. In cigarette smokers, transdermal nicotine patches (TNP) can control nicotine craving, but the effects of nicotine patches on RAC binding are unknown. Thus, we sought to determine the test-retest reliability of RAC binding in the presence of nicotine patches.
Methods: Eleven male smokers were scanned twice with RAC on separate days while wearing TNP.
Results: Across the striatum, test-retest variability was 7.63 ± 5.88; percent change in binding potential was 1.11 ± 9.83; and the intraclass correlation coefficient was 0.91 (p < 0.0001).
Conclusion: Baseline RAC binding is highly reproducible in smokers wearing nicotine patches. This suggests that TNP are an acceptable method for controlling cigarette craving during studies that utilize RAC to examine changes in dopamine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yoder KK, Kareken DA, Morris ED. Assessing Dopaminergic Neurotransmission with PET: Basic Theory and Applications in Alcohol Research. Current Medical Imaging Reviews. 2011 in press.
-
- Laruelle M. Imaging synaptic neurotransmission with in vivo binding competition techniques: a critical review. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20:423–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

