The retinoid signalling molecule, TRIM16, is repressed during squamous cell carcinoma skin carcinogenesis in vivo and reduces skin cancer cell migration in vitro
- PMID: 22009481
- PMCID: PMC3504077
- DOI: 10.1002/path.2986
The retinoid signalling molecule, TRIM16, is repressed during squamous cell carcinoma skin carcinogenesis in vivo and reduces skin cancer cell migration in vitro
Abstract
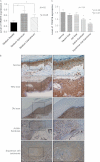
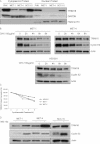
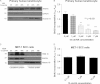
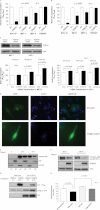
Retinoid therapy is used for chemo-prevention in immuno-suppressed patients at high risk of developing skin cancer. The retinoid signalling molecule, tripartite motif protein 16 (TRIM16), is a regulator of keratinocyte differentiation and a tumour suppressor in retinoid-sensitive neuroblastoma. We sought to determine the role of TRIM16 in skin squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) pathogenesis. We have shown that TRIM16 expression was markedly reduced during the histological progression from normal skin to actinic keratosis and SCC. SCC cell lines exhibited lower cytoplasmic and nuclear TRIM16 expression compared with primary human keratinocyte (PHK) cells due to reduced TRIM16 protein stability. Overexpressed TRIM16 translocated to the nucleus, inducing growth arrest and cell differentiation. In SCC cells, TRIM16 bound to and down regulated nuclear E2F1, this is required for cell replication. Retinoid treatment increased nuclear TRIM16 expression in retinoid-sensitive PHK cells, but not in retinoid-resistant SCC cells. Overexpression of TRIM16 reduced SCC cell migration, which required the C-terminal RET finger protein (RFP)-like domain of TRIM16. The mesenchymal intermediate filament protein, vimentin, was directly bound and down-regulated by TRIM16 and was required for TRIM16-reduced cell migration. Taken together, our data suggest that loss of TRIM16 expression plays an important role in the development of cutaneous SCC and is a determinant of retinoid sensitivity.
Copyright © 2011 Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Armstrong BK, Kricker A. The epidemiology of UV induced skin cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2001;63:8–18. - PubMed
-
- Halliday GM, Norval M, Byrne SN, et al. The effects of sunlight on the skin. Drug Discov Today: Disease Mechanisms. 2008;5:e201–e209.
-
- Lotan R, Xu XC, Lippman SM, et al. Suppression of retinoic acid receptor-beta in premalignant oral lesions and its up-regulation by isotretinoin. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1405–1410. - PubMed
-
- Cheung B, Hocker JE, Smith SA, et al. Retinoic acid receptors beta and gamma distinguish retinoid signals for growth inhibition and neuritogenesis in human neuroblastoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;229:349–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

