Dynamic contrast enhanced-magnetic resonance imaging study of the nutrition pathway for lumbar intervertebral disk cartilage of normal goats
- PMID: 22009595
- PMCID: PMC6583276
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1757-7861.2011.00123.x
Dynamic contrast enhanced-magnetic resonance imaging study of the nutrition pathway for lumbar intervertebral disk cartilage of normal goats
Abstract
Objective: Study of the nutrition pathway for lumbar intervertebral disk cartilage of normal goats.
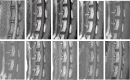
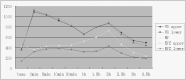
Methods: Four lumbar intervertebral disks from each of eight 24-month-old goats (32 disks) were studied. After the goats had been anesthetized, signal intensity changes in the regions of interest (ROI) were observed by dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance scanning. Before and after enhancement at the time points of 0, 5, 10, and 30 mins, and 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, and 3.5 hs, the ROI signal intensity was measured, and the time-signal intensity curve and peak times analyzed.
Results: Signal intensity in the vertebral bodies reached a peak at 0 min and decreased quickly thereafter. Signal intensity in the cartilage endplate zones reached the first peak at 30 mins and then went down slightly before increasing to a second peak at 2 hs. Signal intensity in the nuclei pulposus was negative within 5 mins, increased slowly to a peak at 2 hs, and declined thereafter.
Conclusion: Nutrient metabolism of the lumbar intervertebral disks of normal goats occurs mainly through the cartilage end-plate pathway.
© 2011 Tianjin Hospital and Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Adams MA, Roughley PJ. What is intervertebral disk degeneration, and what causes it? Spine, 2006, 31: 2151–2161. - PubMed
-
- Andersson GB. Epidemiology of low back pain. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl, 1998, 281: 28–31. - PubMed
-
- Adams MA, Freeman BJ, Morrison HP, et al Mechanical initiation of intervertebral disk degeneration. Spine, 2000, 25: 1625–1636. - PubMed
-
- Gruber HE, Hanley EN Jr. Recent advances in disk cell biology. Spine, 2003, 28: 186–193. - PubMed
-
- Nerlich AG, Schleicher ED, Boos N. 1997 Volvo Award winner in basic science studies. immunohistologic markers for age‐related changes of human lumbar intervertebral discs. Spine, 1997, 22: 2781–2795. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

