Sonoanatomy relevant for ultrasound-guided central neuraxial blocks via the paramedian approach in the lumbar region
- PMID: 22010025
- PMCID: PMC3474051
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr/93508121
Sonoanatomy relevant for ultrasound-guided central neuraxial blocks via the paramedian approach in the lumbar region
Abstract
Objectives: The use of ultrasound to guide peripheral nerve blocks is now a well-established technique in regional anaesthesia. However, despite reports of ultrasound guided epidural access via the paramedian approach, there are limited data on the use of ultrasound for central neuraxial blocks, which may be due to a poor understanding of spinal sonoanatomy. The aim of this study was to define the sonoanatomy of the lumbar spine relevant for central neuraxial blocks via the paramedian approach.
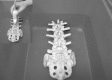
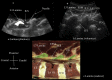
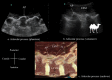
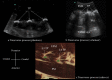
Methods: The sonoanatomy of the lumbar spine relevant for central neuraxial blocks via the paramedian approach was defined using a "water-based spine phantom", young volunteers and anatomical slices rendered from the Visible Human Project data set.
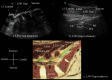
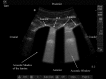
Results: The water-based spine phantom was a simple model to study the sonoanatomy of the osseous elements of the lumbar spine. Each osseous element of the lumbar spine, in the spine phantom, produced a "signature pattern" on the paramedian sagittal scans, which was comparable to its sonographic appearance in vivo. In the volunteers, despite the narrow acoustic window, the ultrasound visibility of the neuraxial structures at the L3/L4 and L4/L5 lumbar intervertebral spaces was good, and we were able to delineate the sonoanatomy relevant for ultrasound-guided central neuraxial blocks via the paramedian approach.
Conclusion: Using a simple water-based spine phantom, volunteer scans and anatomical slices from the Visible Human Project (cadaver) we have described the sonoanatomy relevant for ultrasound-guided central neuraxial blocks via the paramedian approach in the lumbar region.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gelatin-agar lumbosacral spine phantom: a simple model for learning the basic skills required to perform real-time sonographically guided central neuraxial blocks.J Ultrasound Med. 2011 Feb;30(2):263-72. doi: 10.7863/jum.2011.30.2.263. J Ultrasound Med. 2011. PMID: 21266566
-
Sonoanatomy relevant for lumbar plexus block in volunteers correlated with cross-sectional anatomic and magnetic resonance images.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2013 Sep-Oct;38(5):391-7. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0b013e31829e52cc. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2013. PMID: 23974865
-
Ultrasonography of the lumbar spine for neuraxial and lumbar plexus blocks.Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2011 Oct;24(5):567-72. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0b013e32834aa234. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2011. PMID: 21822134 Review.
-
Ultrasound-guided Pararadicular Injection in the Lumbar Spine: A Comparative Study of the Paramedian Sagittal and Paramedian Sagittal Oblique Approaches.Pain Pract. 2015 Nov;15(8):693-700. doi: 10.1111/papr.12249. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Pain Pract. 2015. PMID: 25313534 Clinical Trial.
-
Ultrasonography of the adult thoracic and lumbar spine for central neuraxial blockade.Anesthesiology. 2011 Jun;114(6):1459-85. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e318210f9f8. Anesthesiology. 2011. PMID: 21422997 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound Phantoms to Protect Patients from Novices.Korean J Pain. 2016 Apr;29(2):73-7. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.2.73. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Korean J Pain. 2016. PMID: 27103961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preprocedural Ultrasound Estimates of Epidural Depth: Transverse Median Plane is Comparable to Paramedian Sagittal Oblique Plane in Non-Pregnant Patients.Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2020 Feb;48(1):31-37. doi: 10.5152/TJAR.2019.92342. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2020. PMID: 32076677 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-guided periradicular oxygen-ozone injections as a treatment option for low back pain associated with sciatica.Int Orthop. 2021 May;45(5):1239-1246. doi: 10.1007/s00264-021-04975-w. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Int Orthop. 2021. PMID: 33629173
-
Real-time ultrasound-guided mid-thoracic epidural access using a novel paramedian cross (PX) view and drip infusion technique: a brief technical report.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2024 Nov 4;49(11):840-844. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2023-105071. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2024. PMID: 38388009 Free PMC article.
-
A pictorial review of signature patterns living in musculoskeletal ultrasonography.Korean J Pain. 2016 Oct;29(4):217-228. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.4.217. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Korean J Pain. 2016. PMID: 27738500 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Karmakar MK, Kwok WH, Ho AM, Tsang K, Chui PT, Gin T. Ultrasound-guided sciatic nerve block: description of a new approach at the subgluteal space. Br J Anaesth 2007;98:390–5 - PubMed
-
- Karmakar MK, Ho AM, Li X, Kwok WH, Tsang K, Kee WD. Ultrasound-guided lumbar plexus block through the acoustic window of the lumbar ultrasound trident. Br J Anaesth 2008;100:533–7 - PubMed
-
- Mathieu S, Dalgleish DJ. A survey of local opinion of NICE guidance on the use of ultrasound in the insertion of epidural catheters. Anaesthesia 2008;63:1146–7 - PubMed
-
- Grau T, Leipold RW, Conradi R, Martin E, Motsch J. Ultrasound imaging facilitates localization of the epidural space during combined spinal and epidural anaesthesia. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2001;26:64–7 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

