Therapeutic potential of melatonin and its analogs in Parkinson's disease: focus on sleep and neuroprotection
- PMID: 22010042
- PMCID: PMC3187674
- DOI: 10.1177/1756285611406166
Therapeutic potential of melatonin and its analogs in Parkinson's disease: focus on sleep and neuroprotection
Abstract
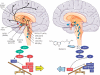
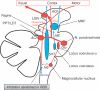
Sleep disorders constitute major nonmotor features of Parkinson's disease (PD) that have a substantial effect on patients' quality of life and can be related to the progression of the neurodegenerative disease. They can also serve as preclinical markers for PD, as it is the case for rapid eye movement (REM)-associated sleep behavior disorder (RBD). Although the etiology of sleep disorders in PD remains undefined, the assessment of the components of the circadian system, including melatonin secretion, could give therapeutically valuable insight on their pathophysiopathology. Melatonin is a regulator of the sleep/wake cycle and also acts as an effective antioxidant and mitochondrial function protector. A reduction in the expression of melatonin MT(1) and MT(2) receptors has been documented in the substantia nigra of PD patients. The efficacy of melatonin for preventing neuronal cell death and for ameliorating PD symptoms has been demonstrated in animal models of PD employing neurotoxins. A small number of controlled trials indicate that melatonin is useful in treating disturbed sleep in PD, in particular RBD. Whether melatonin and the recently developed melatonergic agents (ramelteon, tasimelteon, agomelatine) have therapeutic potential in PD is also discussed.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; REM sleep behavior disorder; agomelatine; insomnia; light therapy; melatonin; oxidative stress; ramelteon; tasimelteon.
Figures
References
-
- Acuña-Castroviejo D., Coto-Montes A., Gaia M.M., Ortiz G.G., Reiter R.J. (1997) Melatonin is protective against MPTP-induced striatal and hippocampal lesions. Life Sci 60: L23–L29 - PubMed
-
- Acuña Castroviejo D., Lopez L.C., Escames G., Lopez A., Garcia J.A., Reiter R.J. (2011) Melatonin-mitochondria Interplay in health and disease. Curr Top Med Chem 11: 221–240 - PubMed
-
- Adi N., Mash D.C., Ali Y., Singer C., Shehadeh L., Papapetropoulos S. (2010) Melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptor expression in Parkinson's disease. Med Sci Monit 16: BR61–BR67 - PubMed
-
- Adler C.H. (2005) Nonmotor complications in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 20(Suppl. 11): S23–S29 - PubMed
-
- Adler C.H., Thorpy M.J. (2005) Sleep issues in Parkinson's disease. Neurology 64: S12–S20 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

