Loci affecting gamma-glutamyl transferase in adults and adolescents show age × SNP interaction and cardiometabolic disease associations
- PMID: 22010049
- PMCID: PMC3276286
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddr478
Loci affecting gamma-glutamyl transferase in adults and adolescents show age × SNP interaction and cardiometabolic disease associations
Abstract
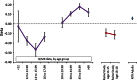
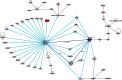
Serum gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) activity is a marker of liver disease which is also prospectively associated with the risk of all-cause mortality, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes and cancers. We have discovered novel loci affecting GGT in a genome-wide association study (rs1497406 in an intergenic region of chromosome 1, P = 3.9 × 10(-8); rs944002 in C14orf73 on chromosome 14, P = 4.7 × 10(-13); rs340005 in RORA on chromosome 15, P = 2.4 × 10(-8)), and a highly significant heterogeneity between adult and adolescent results at the GGT1 locus on chromosome 22 (maximum P(HET) = 5.6 × 10(-12) at rs6519520). Pathway analysis of significant and suggestive single-nucleotide polymorphism associations showed significant overlap between genes affecting GGT and those affecting common metabolic and inflammatory diseases, and identified the hepatic nuclear factor (HNF) family as controllers of a network of genes affecting GGT. Our results reinforce the disease associations of GGT and demonstrate that control by the GGT1 locus varies with age.
© The Author 2011. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang H., Forman H.J., Choi J. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in glutathione biosynthesis. Methods Enzymol. 2005;401:468–483. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(05)01028-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Whitfield J.B. Gamma glutamyl transferase. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab Sci. 2001;38:263–355. doi:10.1080/20014091084227. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kazemi-Shirazi L., Endler G., Winkler S., Schickbauer T., Wagner O., Marsik C. Gamma glutamyltransferase and long-term survival: is it just the liver? Clin. Chem. 2007;53:940–946. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2006.081620. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fraser A., Harris R., Sattar N., Ebrahim S., Smith G.D., Lawlor D.A. Gamma-glutamyltransferase is associated with incident vascular events independently of alcohol intake: analysis of the British Women's Heart and Health Study and Meta-Analysis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007;27:2729–2735. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.152298. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fraser A., Harris R., Sattar N., Ebrahim S., Davey Smith G., Lawlor D.A. Alanine aminotransferase, gamma-glutamyltransferase, and incident diabetes: the British Women's Heart and Health Study and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:741–750. doi:10.2337/dc08-1870. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DA019951/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05 AA017688/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA13320/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA13321/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- DA012854/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AA07728/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 MH068457-06/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AA14041/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA07535/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA13326/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- 166067/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- AA17688/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA11998/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01D0042157-01A/PHS HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

