Impaired wound healing in hypoxic renal tubular cells: roles of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and glycogen synthase kinase 3β/β-catenin signaling
- PMID: 22010210
- PMCID: PMC3251027
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.111.187427
Impaired wound healing in hypoxic renal tubular cells: roles of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and glycogen synthase kinase 3β/β-catenin signaling
Abstract
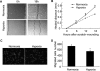
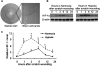
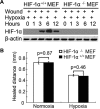
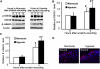
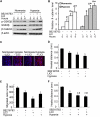
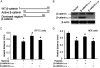
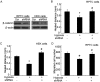
Wound and subsequent healing are frequently associated with hypoxia. Although hypoxia induces angiogenesis for tissue remodeling during wound healing, it may also affect the healing response of parenchymal cells. Whether and how wound healing is affected by hypoxia in kidney cells and tissues is currently unknown. Here, we used scratch-wound healing and transwell migration models to examine the effect of hypoxia in cultured renal proximal tubular cells (RPTC). Wound healing and migration were significantly slower in hypoxic (1% oxygen) RPTC than normoxic (21% oxygen) cells. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) was induced during scratch-wound healing in normoxia, and the induction was more evident in hypoxia. Nevertheless, HIF-1α-null and wild-type cells healed similarly after scratch wounding. Moreover, activation of HIF-1α with dimethyloxalylglycine in normoxic cells did not suppress wound healing, negating a major role of HIF-1α in wound healing in this model. Scratch-wound healing was also associated with glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β)/β-catenin signaling, which was further enhanced by hypoxia. Pharmacological inhibition of GSK3β resulted in β-catenin expression, accompanied by the suppression of wound healing and transwell cell migration. Ectopic expression of β-catenin in normoxic cells could also suppress wound healing, mimicking the effect of hypoxia. Conversely, inhibition of β-catenin via dominant negative mutants or short hairpin RNA improved wound healing and transwell migration in hypoxic cells. The results suggest that GSK3β/β-catenin signaling may contribute to defective wound healing in hypoxic renal cells and tissues.
Figures

References
-
- Bernhardt WM, Câmpean V, Kany S, Jürgensen JS, Weidemann A, Warnecke C, Arend M, Klaus S, Günzler V, Amann K, et al. (2006) Preconditional activation of hypoxia-inducible factors ameliorates ischemic acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1970–1978 - PubMed
-
- Brembeck FH, Rosário M, Birchmeier W. (2006) Balancing cell adhesion and Wnt signaling, the key role of β-catenin. Curr Opin Genet Dev 16:51–59 - PubMed
-
- Carroll TJ, Park JS, Hayashi S, Majumdar A, McMahon AP. (2005) Wnt9b plays a central role in the regulation of mesenchymal to epithelial transitions underlying organogenesis of the mammalian urogenital system. Dev Cell 9:283–292 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

