New strategies for treatment of ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancers
- PMID: 22010214
- PMCID: PMC3477548
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1404
New strategies for treatment of ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancers
Abstract
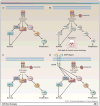
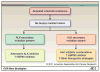
The identification of oncogenic alterations in subsets of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is transforming clinical care. Genomic rearrangements in anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) are detected in 3% to 7% of patients with NSCLC. The ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitor crizotinib has demonstrated clinical efficacy in ALK-rearranged NSCLC patients and was recently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Crizotinib is currently under additional phase III clinical development as both initial and second-line therapy for advanced ALK-rearranged NSCLC. However, new challenges in the diagnosis and treatment of this subset of NSCLC have emerged, including the need to determine the most effective means of diagnosing ALK-rearranged NSCLC and the emergence of acquired drug resistance to crizotinib. In this review, we discuss current strategies for treatment and diagnosis, as well as the current knowledge about mechanisms of acquired resistance to crizotinib. Finally, we discuss the strategies that are underway to clinically overcome acquired drug resistance.
©2011 AACR.
Figures
References
-
- Morris SW, Kirstein MN, Valentine MB, Dittmer KG, Shapiro DN, Saltman DL, et al. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science. 1994;263:1281–4. - PubMed
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

