Kudzu root extract does not perturb the sleep/wake cycle of moderate drinkers
- PMID: 22010780
- PMCID: PMC3233215
- DOI: 10.1089/acm.2010.0540
Kudzu root extract does not perturb the sleep/wake cycle of moderate drinkers
Abstract
Objectives: According to ancient Chinese medicine, kudzu root has been used as an ingredient to treat alcohol intoxication for centuries. Kudzu root extract is effective at reducing alcohol intake in animals and in humans, both in a natural-settings laboratory environment and on an outpatient basis. In dependent populations, withdrawal from alcohol is associated with disturbed sleep. These disturbances to the quantity and quality of sleep likely impact relapse to drinking. Many medications used to treat alcohol dependence also affect sleep. Therefore, as a possible treatment for alcohol dependence, the impact of kudzu root extract on the sleep/wake cycle is an important aspect of its effectiveness.
Design: This double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial tested the effects of kudzu root extract on the sleep/wake cycles of moderate drinkers.
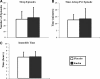
Results: Kudzu extract had no effect on any of the sleep parameters measured, including sleep efficiency, sleep latency, total time asleep per night, number of waking episodes, time awake per episode, number of moving minutes, number of sleep episodes, time asleep per episode, and number of immobile minutes.
Conclusions: These data suggest that the administration of kudzu root extract does not disturb sleep/wake cycles of moderate drinkers, and as such its utility as an adjunct treatment for alcohol dependence remains free of any potential side-effects on sleep.
Figures



References
-
- Overstreet DH. Lee YW. Rezvani AH, et al. Suppression of alcohol intake after administration of the Chinese herbal medicine, NPI-028, and its derivatives. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996;20:221–227. - PubMed
-
- Overstreet D. Yee Y-W. Chen Y, et al. The Chinese herbal medicine NPI-028 suppresses alcohol intake in alcohol-preferring rats and monkeys without inducing taste aversion. J Perfusion. 1998;11:381–389.
-
- Heyman GM. Keung WM. Vallee BL. Daidzin decreases ethanol consumption in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996;20:1083–1087. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

