Ultrasensitive measurements of microbial rhodopsin photocycles using photochromic FRET
- PMID: 22010969
- PMCID: PMC3253248
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.2011.01011.x
Ultrasensitive measurements of microbial rhodopsin photocycles using photochromic FRET
Abstract
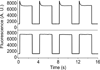
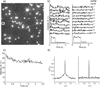
Microbial rhodopsins are an important class of light-activated transmembrane proteins whose function is typically studied on bulk samples. Herein, we apply photochromic fluorescence resonance energy transfer to investigate the dynamics of these proteins with sensitivity approaching the single-molecule limit. The brightness of a covalently linked organic fluorophore is modulated by changes in the absorption spectrum of the endogenous retinal chromophore that occur as the molecule undergoes a light-activated photocycle. We studied the photocycles of blue-absorbing proteorhodopsin and sensory rhodopsin II (SRII). Clusters of 2-3 molecules of SRII clearly showed a light-induced photocycle. Single molecules of SRII showed a photocycle upon signal averaging over several illumination cycles.
© 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Photochemistry and Photobiology © 2011 The American Society of Photobiology.
Figures



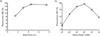
References
-
- Ruiz-Gonzalez MX, Marin I. New insights into the evolutionary history of type 1 rhodopsins. J. Mol. Evol. 2004;58:348–358. - PubMed
-
- Sharma AK, Spudich JL, Doolittle WF. Microbial rhodopsins: functional versatility and genetic mobility. Trends Microbiol. 2006;14:463–469. - PubMed
-
- Fuhrman JA, Schwalbach MS, Stingl U. Proteorhodopsins: an array of physiological roles? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008;6:488–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

