Maternal protein restriction reduces expression of angiotensin I-converting enzyme 2 in rat placental labyrinth zone in late pregnancy
- PMID: 22011389
- PMCID: PMC3290663
- DOI: 10.1095/biolreprod.111.094607
Maternal protein restriction reduces expression of angiotensin I-converting enzyme 2 in rat placental labyrinth zone in late pregnancy
Abstract
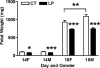
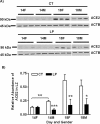
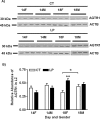
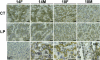
Both the systemic and the uteroplacental renin-angiotensin system (RAS) display dramatic changes during pregnancy. However, whether gestational protein insufficiency affects the expressions of RAS in the placenta remains unknown. In this study, we hypothesized that the expression of Ace2 in the placental labyrinth was reduced by maternal protein restriction. Pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats were fed a normal diet or a low-protein diet (LP) from Day 1 of pregnancy until they were killed at Day 14 or Day 18. The labyrinth zone (LZ) of the placenta was then dissected and snap frozen for expression analysis by quantitative real-time PCR of Ace, Ace2, Agtr1a, Agtr1b, and Agtr2. Formalin-fixed placentas were used for immunohistochemical analysis on ACE and ACE2 proteins. The findings include 1) the expression of Ace2 in rat LZ was reduced by maternal protein restriction in late pregnancy; 2) ACE protein was mainly present in syncytiotrophoblasts, whereas ACE2 protein was found predominantly in fetal mesenchymal tissue and fetal capillaries; 3) Agtr1a was predominant in the rat LZ, and its mRNA levels, but not protein levels, were reduced by LP; 4) expressions of Ace, Ace2, and Agtr1a in the rat LZ and their response to LP occurred in a gender-dependent manner. These results may indicate that a reduced expression of Ace2 and perhaps an associated reduction in angiotensin (1-7) production in the placenta by maternal protein restriction may be responsible for fetal growth restriction and associated programming of adulthood hypertension.
Figures


References
-
- Moritz KM, Johnson K, Douglas-Denton R, Wintour EM, Dodic M. Maternal glucocorticoid treatment programs alterations in the renin-angiotensin system of the ovine fetal kidney. Endocrinology 2002; 143: 4455 4463 - PubMed
-
- Wyrwoll CS, Mark PJ, Mori TA, Puddey IB, Waddell BJ. Prevention of programmed hyperleptinemia and hypertension by postnatal dietary omega-3 fatty acids. Endocrinology 2006; 147: 599 606 - PubMed
-
- Gilbert JS, Ford SP, Lang AL, Pahl LR, Drumhiller MC, Babcock SA, Nathanielsz PW, Nijland MJ. Nutrient restriction impairs nephrogenesis in a gender-specific manner in the ovine fetus. Pediatr Res 2007; 61: 42 47 - PubMed
-
- Langley-Evans SC, Welham SJ, Jackson AA. Fetal exposure to a maternal low protein diet impairs nephrogenesis and promotes hypertension in the rat. Life Sci 1999; 64: 965 974 - PubMed
-
- Grigore D, Ojeda NB, Robertson EB, Dawson AS, Huffman CA, Bourassa EA, Speth RC, Brosnihan KB, Alexander BT. Placental insufficiency results in temporal alterations in the renin angiotensin system in male hypertensive growth restricted offspring. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2007; 293: R804 R811 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

