Bovine AAV transcytosis inhibition by tannic acid results in functional expression of CFTR in vitro and altered biodistribution in vivo
- PMID: 22011646
- PMCID: PMC3266448
- DOI: 10.1038/gt.2011.138
Bovine AAV transcytosis inhibition by tannic acid results in functional expression of CFTR in vitro and altered biodistribution in vivo
Abstract
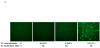
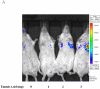
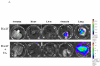
Bovine adeno-associated virus (BAAV) can enter a cell either through a transcytosis or transduction pathway. We previously demonstrated that particles entering via the transcytosis pathway can be redirected to transduce the cell by blocking particle exocytosis with tannic acid (TA). To investigate whether this approach is useful in lung gene therapy applications, we tested the effect of TA on BAAV transduction in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia in vitro, and in mouse lung in vivo. Our findings suggest that BAAV transcytosis can occur in vivo and that treatment with TA reduces transcytosis and increases lung transduction. TA treatment did not impair the sorting and the activity of the BAAV expressed cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator membrane protein.
Figures













References
-
- Di Pasquale G, Chiorini JA. AAV transcytosis through barrier epithelia and endothelium. Mol Ther. 2006;13(3):506–16. - PubMed
-
- Walters RW, Pilewski JM, Chiorini JA, Zabner J. Secreted and transmembrane mucins inhibit gene transfer with AAV4 more efficiently than AAV5. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(26):23709–13. - PubMed
-
- Polishchuk R, Di Pentima A, Lippincott-Schwartz J. Delivery of raft-associated, GPI-anchored proteins to the apical surface of polarized MDCK cells by a transcytotic pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6(4):297–307. - PubMed
-
- Yui N, Okutsu R, Sohara E, Rai T, Ohta A, Noda Y, et al. FAPP2 is required for aquaporin-2 apical sorting at trans-Golgi network in polarized MDCK cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009;297(6):C1389–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

