MicroRNA modulation of cholesterol homeostasis
- PMID: 22011750
- PMCID: PMC3298754
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.226688
MicroRNA modulation of cholesterol homeostasis
Abstract
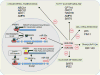
Although the roles of the sterol response element binding protein-1 (SREBP1) and SREBP2 transcription factors in regulating fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis and uptake have been known for some time, it was recently discovered that 2 related microRNAs (miRs), miR-33a and miR-33b, are embedded in these genes. Studies indicate that miR-33a and miR-33b act with their host genes, Srebp2 and Srebp1, respectively, to reciprocally regulate cholesterol homeostasis and fatty acid metabolism in a negative feedback loop. miR-33 has been shown to posttranscriptionally repress key genes involved in cellular cholesterol export and high-density lipoprotein metabolism (Abca1, Abcg1, Npc1), fatty acid oxidation (Crot, Cpt1a, Hadhb, Ampk), and glucose metabolism (Sirt6, Irs2). Delivery of inhibitors of miR-33 in vitro and in vivo relieves repression of these genes, resulting in upregulation of the associated metabolic pathways. In mouse models, miR-33 antagonism has proven to be an effective strategy for increasing plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and fatty acid oxidation and protecting from atherosclerosis. These exciting findings have opened up promising new avenues for the development of therapeutics to treat dyslipidemia and other metabolic disorders.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNAs in metabolism and metabolic diseases.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2011;76:225-33. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2011.76.011049. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2011. PMID: 22156303 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs regulating lipid metabolism in atherogenesis.Thromb Haemost. 2012 Apr;107(4):642-7. doi: 10.1160/TH11-10-0694. Epub 2012 Jan 25. Thromb Haemost. 2012. PMID: 22274626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of miR-33a/b in non-human primates raises plasma HDL and lowers VLDL triglycerides.Nature. 2011 Oct 19;478(7369):404-7. doi: 10.1038/nature10486. Nature. 2011. PMID: 22012398 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cholesterol and bile acid homeostasis by the cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase/steroid response element-binding protein 2/microRNA-33a axis in mice.Hepatology. 2013 Sep;58(3):1111-21. doi: 10.1002/hep.26427. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23536474 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in lipid metabolism.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2011 Apr;22(2):86-92. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e3283428d9d. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2011. PMID: 21178770 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Relationships among injury, fibrosis, and time in human kidney transplants.JCI Insight. 2016 Jan 21;1(1):e85323. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.85323. JCI Insight. 2016. PMID: 27699214 Free PMC article.
-
XenomiRs and miRNA homeostasis in health and disease: evidence that diet and dietary miRNAs directly and indirectly influence circulating miRNA profiles.RNA Biol. 2012 Sep;9(9):1147-54. doi: 10.4161/rna.21619. Epub 2012 Sep 1. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 22951590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay of mitochondrial metabolism and microRNAs.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Feb;74(4):631-646. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2342-7. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27563705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory element-binding factor 1 (Srebf1) exhibit reduced HDL-C in vivo.Sci Rep. 2014 Jun 16;4:5312. doi: 10.1038/srep05312. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24931346 Free PMC article.
-
Association between ErbB3 genetic polymorphisms and coronary artery disease in the Han and Uyghur populations of China.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Sep 15;8(9):16520-7. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26629179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambros V. MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell. 2003;113:673–676. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:102–114. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

